Data Structures and Algorithms - Unit Wise Questions
1. What is stack? What are the different applications of stack? Explain stack operations with example.(1 + 3 + 7)
AI is thinking...
2. Differentiate between singly linked list and doubly linked list. How do you insert and delete a node from doubly linked list? Explain.(3+7)
AI is thinking...
3. What is shortest path? Explain Dijkstra algorithm for finding shortest path using suitable example.(2+8)
AI is thinking...
4. How do you find complexity of algorithms? Explain.
AI is thinking...
4. What is dynamic memory allocation? Compare data structure with abstract data type.(2+3)
AI is thinking...
4. What are the difference between two dimension array and multidimension array?
Two dimension (2D) array:
A two-dimensional array is nothing but a matrix, that has rows and columns in it. For e.g.
int a[3][4];
float b[10][10];
Multidimensional array :
Any array which has a dimension higher than One is a multidimensional array. 2D array is also a multidimensional array.
E.g. of 3D array
int a[3][2][4];
Here, the first subscript specifies a plane number, the second subscript a row number and the third a column number.
DIFFERENCE :
Every 2D array is a multidimensional array but the other way round is not necessary(for example a 3D array is also a multidimensional array but its surely not 2D).
AI is thinking...
4. Discuss array as an ADT.
Let A be an array of type T and has n elements then it satisfied the following operations:
- CREATE(A): Create an array A
- INSERT(A,X): Insert an element X into an array A in any location
- DELETE(A,X): Delete an element X from an array A
- MODIFY(A,X,Y): modify element X by Y of an array A
- TRAVELS(A): Access all elements of an array A
- MERGE(A,B): Merging elements of A and B into a third array C
Thus by using a one-dimensional array we can perform above operations thus an array acts as an ADT.
AI is thinking...
4. What do you mean by complexity of algorithms? How do you find time complexity?
The complexity of an algorithm is a function f (n) which measures the time and space used by an algorithm in terms of input size n. The complexity of an algorithm is a way to classify how efficient an algorithm is, compared to alternative ones.
The process of finding complexity of given algorithm by counting number of steps and number of memory references used by using RAM model is called detailed analysis. For detailed time complexity algorithm we count the number of steps and finally add all steps and calculate their big oh notation. Similarly for detailed analysis of space complexity we count the number of memory references and finally add all steps and find their big oh notation.
E.g.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, n, fact=1;
printf("Enter a number to calculate factorial:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
fact = fact*i;
printf("Factorial of %d=%d", n, fact);
return 0;
}
Time Complexity:
The declaration statement takes 1 step.
Printf statement takes 1 step.
Scanf statement takes 1 step.
In for loop:
i=1 takes 1 step
i<=n takes (n+1) step
i++ takes n step
within for loop fact=fact*i takes n step
printf statement takes 1 step
return statement takes 1 step
Total time complexity = 1+1+1+1+n+1+n+n+1+1
= 3n+7
= O(n)
Space complexity:
total memory references used = 3 = O(1)
AI is thinking...
4. Differentiate between structure and union.
AI is thinking...
5. What is an algorithm? What is to analyze in algorithm? Define Big Oh notation for time complexity measurement of algorithm.
An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions used for solving a problem, which can be implemented (as a program) on a computer
Algorithms are used to convert our problem solution into step by step statements. These statements can be converted into computer programming instructions which forms a program. This program is executed by computer to produce solution. Here, program takes required data as input, processes data according to the program instructions and finally produces result as shown in the following picture
The analysis of algorithms is the process of finding the computational complexity of algorithms – the amount of time, storage, or other resources needed to execute them.
Big Oh notation
A function f(n) is said to be “big-Oh of g(n)” and we write, f(n)=O(g(n)) or simply f=O(g), if there are two positive constants c and n0 such that f(n)<=c*g(n) for all n>=n0.
E.g. The big oh notation of f(n)=n+4 is O(n) since n+4<=2n for all n>=4.
The big oh notation of f(n)=n2+3n+4 is O(n2) since n2+3n+4<=2n2 for all n>=4.
Big O notation specifically describes worst case scenario. It represents the upper bound running time complexity of an algorithm.
AI is thinking...
5. Describe the Big 'O' notation.
Big-O notation signifies the relationship between the input to the algorithm and the steps required to execute the algorithm.
A function f(n) is said to be “big-Oh of g(n)” and we write, f(n)=O(g(n)) or simply f=O(g), if there are two positive constants c and n0 such that f(n)<=c*g(n) for all n>=n0.
E.g. The big oh notation of f(n)=n+4 is O(n) since n+4<=2n for all n>=4.
The big oh notation of f(n)=n2+3n+4 is O(n2) since n2+3n+4<=2n2 for all n>=4.
Big O notation specifically describes worst case scenario. It represents the upper bound running time complexity of an algorithm.
AI is thinking...
5. What are the major characteristics of algorithms?
An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions used for solving a problem, which can be implemented (as a program) on a computer
Algorithms are used to convert our problem solution into step by step statements. These statements can be converted into computer programming instructions which forms a program. This program is executed by computer to produce solution. Here, program takes required data as input, processes data according to the program instructions and finally produces result as shown in the following picture

- Input - Every algorithm must take zero or more number of input values from external.
- Output - Every algorithm must produce an output as result.
- Definiteness - Every statement/instruction in an algorithm must be clear and unambiguous (only one interpretation)
- Finiteness - For all different cases, the algorithm must produce result within a finite number of steps.
- Effectiveness - Every instruction must be basic enough to be carried out and it also must be feasible.
- Correctness: Correct set of output values must be produced from the each set of inputs.
AI is thinking...
5. “To write an efficient program, we should know about data structures.” Explain the above statement.
AI is thinking...
5. Explain algorithm for evaluation of postfix expression using stack.(5)
AI is thinking...
5. Differentiate between array and pointer with example.
Array in C is used to store elements of same types whereas Pointers are address variables which stores the address of a another variable. Now array variable is also having a address which can be pointed by a pointer and array can be navigated using pointer. Benefit of using pointer for array is two folds, first, we store the address of dynamically allocated array to the pointer and second, to pass the array to a function. Following are the differences in using array and using pointer to array.
- sizeof() operator prints the size of array in case of array and in case of pointer, it prints the size of int.
- assignment array variable cannot be assigned address of another variable but pointer can take it.
- first value first indexed value is same as value of pointer. For example, array[0] == *p.
- iteration array elements can be navigated using indexes using [], pointer can give access to array elements by using pointer arithmetic. For example, array[2] == *(p+2)
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
void printElement(char* q, int index){
printf("Element at index(%d) is: %c\\n", index, *(q+index));
}
int main() {
char arr[] = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
char* p = arr;
printf("Size of arr[]: %d\\n", sizeof(arr));
printf("Size of p: %d\\n", sizeof(p));
printf("First element using arr is: %c\\n", arr[0]);
printf("First element using p is: %c\\n", *p);
printf("Second element using arr is: %c\\n", arr[1]);
printf("Second element using p is: %c\\n", *(p+1));
printElement(p, 2);
return 0;
}Output:
Size of arr[]: 3
Size of p: 8
First element using arr is: A
First element using p is: A
Second element using arr is: B
Second element using p is: B
Element at index(2) is: C
AI is thinking...
6. Explain queue as an ADT.(5)
AI is thinking...
6. What is an algorithm? Write down the features of an algorithm.
An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions used for solving a problem, which can be implemented (as a program) on a computer
Algorithms are used to convert our problem solution into step by step statements. These statements can be converted into computer programming instructions which forms a program. This program is executed by computer to produce solution. Here, program takes required data as input, processes data according to the program instructions and finally produces result as shown in the following picture
Features of algorithm:
- Input - Every algorithm must take zero or more number of input values from external.
- Output - Every algorithm must produce an output as result.
- Definiteness - Every statement/instruction in an algorithm must be clear and unambiguous (only one interpretation)
- Finiteness - For all different cases, the algorithm must produce result within a finite number of steps.
- Effectiveness - Every instruction must be basic enough to be carried out and it also must be feasible.
- Correctness: Correct set of output values must be produced from the each set of inputs.
AI is thinking...
7. Write a recursive program to find GCD of two numbers.(5)
AI is thinking...
8. What is linked list? How is it different from array?(2+3)
AI is thinking...
9. Hand test bubble sort with array of numbers 53, 42, 78, 3, 5, 2, 15 in ascending order.(4+1)
AI is thinking...
10. What is hashing? Explain concept of hash table and hash function with example.(1 + 4)
AI is thinking...
11. What is Big ‘O’ notation? Analyze any one sorting algorithm.
Big-O notation is a metrics used to find algorithm complexity. Basically, Big-O notation signifies the relationship between the input to the algorithm and the steps required to execute the algorithm.
A function f(n) is said to be “big-Oh of g(n)” and we write, f(n)=O(g(n)) or simply f=O(g), if there are two positive constants c and n0 such that f(n)<=c*g(n) for all n>=n0.
E.g. The big oh notation of f(n)=n+4 is O(n) since n+4<=2n for all n>=4.
The big oh notation of f(n)=n2+3n+4 is O(n2) since n2+3n+4<=2n2 for all n>=4.
Big O notation specifically describes worst case scenario. It represents the upper bound running time complexity of an algorithm.
__________________________________________
Analysis of Selection Sort
Time Complexity:
The selection sort makes first pass in n-1 comparison, the second pass in n-2 comparisons and so on.
Time complexity = (n-1) + (n-2) + (n-3) + …………………………. +2 +1
= O(n2)
Space Complexity:
Since no extra space besides 5 variables is needed for sorting
Space complexity = O(n)
AI is thinking...
11. How to find complexity of algorithms? Explain.
The complexity of an algorithm is a function f (n) which measures the time and space used by an algorithm in terms of input size n. The complexity of an algorithm is a way to classify how efficient an algorithm is, compared to alternative ones.
The process of finding complexity of given algorithm by counting number of steps and number of memory references used by using RAM model is called detailed analysis. For detailed time complexity algorithm we count the number of steps and finally add all steps and calculate their big oh notation. Similarly for detailed analysis of space complexity we count the number of memory references and finally add all steps and find their big oh notation.
E.g.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, n, fact=1;
printf("Enter a number to calculate factorial:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
fact = fact*i;
printf("Factorial of %d=%d", n, fact);
return 0;
}
Time Complexity:
The declaration statement takes 1 step.
Printf statement takes 1 step.
Scanf statement takes 1 step.
In for loop:
i=1 takes 1 step
i<=n takes (n+1) step
i++ takes n step
within for loop fact=fact*i takes n step
printf statement takes 1 step
return statement takes 1 step
Total time complexity = 1+1+1+1+n+1+n+n+1+1
= 3n+7
= O(n)
Space complexity:
total memory references used = 3 = O(1)
AI is thinking...
11. Explain the use of Big O notation in analyzing algorithms. Compare sorting time efficiencies of Quick-Sort and Merge-Sort.
Big-O notation signifies the relationship between the input to the algorithm and the steps required to execute the algorithm.
A function f(n) is said to be “big-Oh of g(n)” and we write, f(n)=O(g(n)) or simply f=O(g), if there are two positive constants c and n0 such that f(n)<=c*g(n) for all n>=n0.
E.g. The big oh notation of f(n)=n+4 is O(n) since n+4<=2n for all n>=4.
The big oh notation of f(n)=n2+3n+4 is O(n2) since n2+3n+4<=2n2 for all n>=4.
Big O notation specifically describes worst case scenario. It represents the upper bound running time complexity of an algorithm.
Quick-Sort vs Merge-Sort
Merge sort is more efficient and works faster than quick sort in case of larger array size or datasets.
whereas
Quick sort is more efficient and works faster than merge sort in case of smaller array size or datasets.
Merge sort has the following performance characteristics:
- Best case:
O(n log n) - Average case:
O(n log n) - Worst case:
O(n log n)
Quicksort has the following performance characteristics:
- Best case:
O(n) - Average case:
O(n log n) - Worst case:
O(n2)
AI is thinking...
11. What is minimum spanning tree? Explain.(5)
AI is thinking...
11. What is dynamic memory allocation? How it is achieved for declaring two dimensional array? Explain.
The process of allocating memory at runtime is known as dynamic memory allocation. Library routines known as memory management functions are used for allocating and freeing memory during execution of a program. These functions are defined in stdlib.h header file.
A 2D array can be dynamically allocated in C using a single pointer. This means that a memory block of size row*column*dataTypeSize is allocated using malloc and pointer arithmetic can be used to access the matrix elements.
A program that demonstrates this is given as follows:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int row = 2, col = 3;
int *arr = (int *)malloc(row * col * sizeof(int));
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < row; i++)
for (j = 0; j < col; j++)
*(arr + i*col + j) = i + j;
printf("The matrix elements are:\\n");
for (i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%d ", *(arr + i*col + j));
}
printf("\\n");
}
free(arr);
return 0;
}
AI is thinking...
11. Justify the statement: “To write an efficient program, we should know about data structures and algorithms”.
AI is thinking...
12. Write short notes on: (2 x 2.5 = 5)
a. Tail recursion b. Collision resolution techniques
AI is thinking...
1. Write a menu program to demonstrate the simulation of stack operations in array implementation.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void push(int);
void pop();
void display();
int stack[SIZE], top = -1;
void main()
{
int value, choice;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n\\n*****
MENU *****\\n");
printf("1.
Push\\n2. Pop\\n3. Display\\n4. Exit");
printf("\\nEnter
your choice: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case 1: printf("Enter the value to be
insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
push(value);
break;
case 2: pop();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nWrong selection!!! Try
again!!!");
}
}
}
void push(int value){
if(top == SIZE-1)
printf("\\nStack
is Full!!! Insertion is not possible!!!");
else{
top++;
stack[top] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion success!!!");
}
}
void pop(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack
is Empty!!! Deletion is not possible!!!");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted
: %d", stack[top]);
top--;
}
}
void display(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack
is Empty!!!");
else{
int i;
printf("\\nStack
elements are:\\n");
for(i=top; i>=0;
i--)
printf("%d\\n",stack[i]);
}
}
AI is thinking...
1. Define stack as ADT. Describe its primitive operations on Array implementation and linked list implementation.
A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items may be inserted and from which items may be deleted at one end, called the top of the stack. The deletion and insertion in a stack is done from top of the stack.
It is a linear data structure which store data temporarily to perform PUSH and POP operation in LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) sequence.

Fig::A stack containing items or elements
Stack as ADT
A stack of elements of type T is a finite sequence of elements of T together with the operations
- CreateEmptyStack(S): Create or make stack S be an empty stack
- Push(S, x): Insert x at one end of the stack, called its top
- Top(S): If stack S is not empty; then retrieve the element at its top
- Pop(S): If stack S is not empty; then delete the element at its top
- IsFull(S): Determine if S is full or not. Return true if S is full stack; return false otherwise
- IsEmpty(S): Determine if S is empty or not. Return true if S is an empty stack; return false otherwise.
Thus by using a stack we can perform above operations thus a stack acts as an ADT.
Primitive operations of stack
The following operations can be performed on a stack:
1. PUSH operation: The push operation is used to add (or push or insert) elements in a Stack.
ü When we add an item to a stack, we say that we push it onto the stack
ü The last item put into the stack is at the top
2. POP operation: The pop operation is used to remove or delete the top element from the stack.
üwe remove an item, we say that we pop item from the stack.
üWhen an item popped, it is always the top item which is removed.
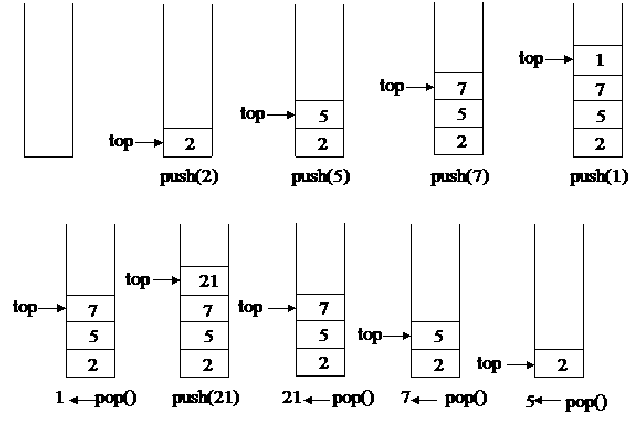
The PUSH and the POP operations are the basic or primitive operations on a stack. Some others operations are:
- CreateEmptyStack operation: This operation is used to create an empty stack.
- IsFull operation: The isfull operation is used to check whether the stack is full or not ( i.e. stack overflow)
- IsEmpty operation: The isempty operation is used to check whether the stack is empty or not. (i. e. stack underflow)
- Top operations: This operation returns the current item at the top of the stack, it doesn’t remove it
AI is thinking...
1. What is stack? How is it different from queue? Write a program to implement all stack operations.
A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items may be inserted and from which items may be deleted at one end, called the top of the stack. The deletion and insertion in a stack is done from top of the stack.
It is a linear data structure which store data temporarily to perform PUSH and POP operation in LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) sequence.
Difference between Stack and Queue

Program to implement stack operations
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void push(int);
void pop();
void display();
int stack[SIZE], top = -1;
void main()
{
int value, choice;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n\\n*****
MENU *****\\n");
printf("1.
Push\\n2. Pop\\n3. Display\\n4. Exit");
printf("\\nEnter
your choice: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case 1: printf("Enter the value to be
insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
push(value);
break;
case 2: pop();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nWrong selection!!! Try
again!!!");
}
}
}
void push(int value){
if(top == SIZE-1)
printf("\\nStack
is Full!!! Insertion is not possible!!!");
else{
top++;
stack[top] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion success!!!");
}
}
void pop(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack
is Empty!!! Deletion is not possible!!!");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted
: %d", stack[top]);
top--;
}
}
void display(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack
is Empty!!!");
else{
int i;
printf("\\nStack
elements are:\\n");
for(i=top; i>=0;
i--)
printf("%d\\n",stack[i]);
}
}
AI is thinking...
1. How can you use stack to convert an infix expression to postfix? Convert infix expression (A + B)*(C - D) to postfix using stack.
Algorithm to convert infix to postfix expression using stack is given below:
1. Scan the infix string from left to right.
2. Initialize an empty stack.
3. If the scanned character is an operand, add it to postfix sting
4. If the scanned character is an operator, PUSH the character to stack.
5. If the top operator in stack has equal or higher precedence than scanned operator then POP the operator present in stack and add it to postfix string else PUSH the scanned character to stack.
6. If the scanned character is a left parenthesis ‘(‘, PUSH it to stack.
7. If the scanned character is a right parenthesis ‘)’, POP and add to postfix string from stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered. Ignore both '(' and ')'.
8. Repeat step 3-7 till all the characters are scanned.
9. After all character are scanned POP the characters and add to postfix string from the stack until it is not empty.
Given,
Infix expression = (A + B)*(C - D)
Converting to postfix:
|
Characters |
stack |
Postfix expression |
|
( |
( |
|
|
A |
( |
A |
|
+ |
(+ |
A |
|
B |
(+ |
AB |
|
) |
|
AB+ |
|
* |
* |
AB+ |
|
( |
*( |
AB+ |
|
C |
*( |
AB+C |
|
- |
*(- |
AB+C |
|
D |
*(- |
AB+CD |
|
) |
* |
AB+CD- |
|
|
|
AB+CD-* |
Postfix expression of given infix is A B + C D - *
AI is thinking...
1. Trace out Infix to Postfix conversion algorithm with given Infix expression.
A + (((B-C) * (D-E) + F)/G) $ (H-I)
Evaluate the postfix expression acquired from above for the given values:
A = 6, B = 2, C = 4, D = 3, E = 8, F = 2, G = 3, H = 5, I = 1.
Given Infix expression.
A + (((B-C) * (D-E) + F)/G) $ (H-I)
Converting it to postfix:
|
Characters |
Stack |
Postfix
expression |
|
A |
|
A |
|
+ |
+ |
A |
|
( |
+( |
A |
|
( |
+(( |
A |
|
( |
+((( |
A |
|
B |
+((( |
AB |
|
- |
+(((- |
AB |
|
C |
+(((- |
ABC |
|
) |
+(( |
ABC- |
|
* |
+((* |
ABC- |
|
( |
+((*( |
ABC- |
|
D |
+((*( |
ABC-D |
|
- |
+((*(- |
ABC-D |
|
E |
+((*(- |
ABC-DE |
|
) |
+((* |
ABC-DE- |
|
+ |
+((+ |
ABC-DE-* |
|
F |
+((+ |
ABC-DE-*F |
|
) |
+( |
ABC-DE-*F+ |
|
/ |
+(/ |
ABC-DE-*F+ |
|
G |
+(/ |
ABC-DE-*F+G |
|
) |
+ |
ABC-DE-*F+G/ |
|
$ |
+$ |
ABC-DE-*F+G/ |
|
( |
+$( |
ABC-DE-*F+G/ |
|
H |
+$( |
ABC-DE-*F+G/H |
|
- |
+$(- |
ABC-DE-*F+G/H |
|
I |
+$(- |
ABC-DE-*F+G/HI |
|
) |
+$ |
ABC-DE-*F+G/HI- |
|
|
+ |
ABC-DE-*F+G/HI-$ |
|
|
|
ABC-DE-*F+G/HI-$+ |
Now,
Evaluating the postfix expression for the given values:
A = 6, B = 2, C = 4, D = 3, E = 8, F = 2, G = 3, H = 5, I = 1
ABC-DE-*F+G/HI-$+
6 2 4 - 3 8 - * 2 +3 / 5 1 - $ +
|
Input symbol |
Stack |
operation |
|
6 |
6 |
|
|
2 |
6, 2 |
|
|
4 |
6, 2, 4 |
|
|
- |
6 |
2
- 4 = -2 |
|
|
6, -2 |
|
|
3 |
6, -2, 3 |
|
|
8 |
6, -2, 3, 8 |
|
|
- |
6, -2 |
3
– 8 = -5 |
|
|
6, -2, -5 |
|
|
* |
6 |
(-2)*(-5)
= 10 |
|
|
6, 10 |
|
|
2 |
6, 10, 2 |
|
|
+ |
6 |
10+2
= 12 |
|
|
6, 12 |
|
|
3 |
6, 12, 3 |
|
|
/ |
6 |
12/3
= 4 |
|
|
6, 4 |
|
|
5 |
6, 4, 5 |
|
|
1 |
6, 4, 5, 1 |
|
|
- |
6, 4 |
5
-1 = 4 |
|
|
6, 4, 4 |
|
|
$ |
6 |
4$4
= 256 |
|
|
6, 256 |
|
|
+ |
|
6
+ 256 = 262 (Result) |
AI is thinking...
2. What is Postfix expression? Write an algorithm to evaluate value of postfix expression. Trace the following expression into postfix expression.
(A+B*C)+(D-E/ F)
The expression in which operator is written in after the operands is called postfix expression. For example: AB+
Algorithm to evaluate value of postfix expression
1. Create a stack to store operands.
2. Scan the given expression from left to right.
3. a) If the scanned character is an operand, push it into the stack.
b) If the scanned character is an operator, POP 2 operands from stack and perform operation and PUSH the result back to the stack.
4. Repeat step 3 till all the characters are scanned.
5. When the expression is ended, the number in the stack is the final result.
Given,
infix expression = (A+B*C)+(D-E/ F)
Now, converting it into postfix:
|
Characters |
stack |
Postfix expression |
|
( |
( |
|
|
A |
( |
A |
|
+ |
(+ |
A |
|
B |
(+ |
AB |
|
* |
(+* |
AB |
|
C |
(+* |
ABC |
|
) |
|
ABC*+ |
|
+ |
+ |
ABC*+ |
|
( |
+( |
ABC*+ |
|
D |
+( |
ABC*+D |
|
- |
+(- |
ABC*+D |
|
E |
+(- |
ABC*+DE |
|
/ |
+(-/ |
ABC*+DE |
|
F |
+(-/ |
ABC*+DEF |
|
) |
+ |
ABC*+DEF/- |
|
|
|
ABC*+DEF/-+ |
The postfix expression of given infix expression is: A B C * + D E F / - +
AI is thinking...
3. Explain the algorithms for infix to postfix conversion and evaluation of postfix expression. Trace the algorithms with suitable example.
Algorithm to convert infix to postfix expression
1. Scan the infix string from left to right.
2. Initialize an empty stack.
3. If the scanned character is an operand, add it to postfix sting
4. If the scanned character is an operator, PUSH the character to stack.
5. If the top operator in stack has equal or higher precedence than scanned operator then POP the operator present in stack and add it to postfix string else PUSH the scanned character to stack.
6. If the scanned character is a left parenthesis ‘(‘, PUSH it to stack.
7. If the scanned character is a right parenthesis ‘)’, POP and add to postfix string from stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered. Ignore both '(' and ')'.
8. Repeat step 3-7 till all the characters are scanned.
9. After all character are scanned POP the characters and add to postfix string from the stack until it is not empty.
Example:
Infix expression: A*B+C
characters | stacks | Postfix expression |
A | A | |
* | * | A |
B | * | AB |
+ | + | AB* |
C | + | AB*C |
AB*C+ |
Postfix expression: AB*C+
Algorithm for evaluation of postfix expression
1. Create a stack to store operands.
2. Scan the given expression from left to right.
3. a) If the scanned character is an operand, push it into the stack.
b) If the scanned character is an operator, POP 2 operands from stack and perform operation and PUSH the result back to the stack.
4. Repeat step 3 till all the characters are scanned.
5. When the expression is ended, the number in the stack is the final result.
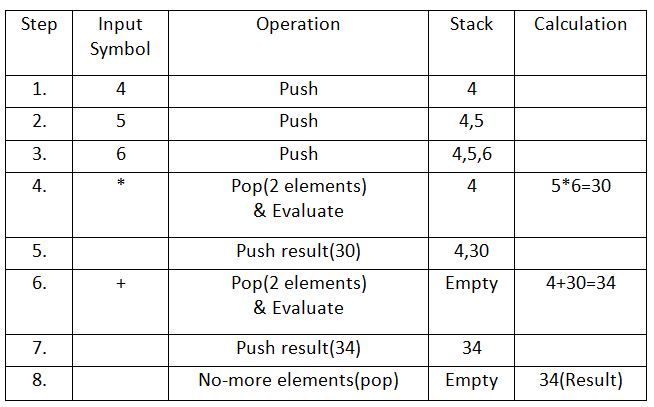
Example:
Let the given expression be “456*+“. We scan all elements one by one.
AI is thinking...
3. Explain In-fix to Postfix Conversion Algorithm. Illustrate it with an example. What changes should be made for converting postfix to prefix.
Algorithm to convert infix to postfix expression
1. Scan the infix string from left to right.
2. Initialize an empty stack.
3. If the scanned character is an operand, add it to postfix sting
4. If the scanned character is an operator, PUSH the character to stack.
5. If the top operator in stack has equal or higher precedence than scanned operator then POP the operator present in stack and add it to postfix string else PUSH the scanned character to stack.
6. If the scanned character is a left parenthesis ‘(‘, PUSH it to stack.
7. If the scanned character is a right parenthesis ‘)’, POP and add to postfix string from stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered. Ignore both '(' and ')'.
8. Repeat step 3-7 till all the characters are scanned.
9. After all character are scanned POP the characters and add to postfix string from the stack until it is not empty.
Example:
Infix expression: A*B+C
characters | stacks | Postfix expression |
A | A | |
* | * | A |
B | * | AB |
+ | + | AB* |
C | + | AB*C |
AB*C+ |
Postfix expression: AB*C+
Now,
To convert postfix to prefix we use following algorithm:
1. Read the Postfix expression from left to right
2. If the symbol is an operand, then push it onto the Stack
3. If the symbol is an operator, then pop two operands from the Stack
Create a string by concatenating the two operands and the operator before them.
string = operator + operand2 + operand1
And push the resultant string back to Stack
4. Repeat the above steps until end of Prefix expression.
AI is thinking...
3. Explain the implementation of stack and queue with example.
Stack
A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items may be inserted and from which items may be deleted at one end, called the top of the stack. The deletion and insertion in a stack is done from top of the stack.
It is a linear data structure which store data temporarily to perform PUSH and POP operation in LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) sequence.

Fig::A stack containing items or elements
Implementation of stack using array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void push(int);
void pop();
void display();
int stack[SIZE], top = -1;
void main()
{
int value, choice;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n\\n***** MENU *****\\n");
printf("1. Push\\n2. Pop\\n3. Display\\n4. Exit");
printf("\\nEnter your choice: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case 1: printf("Enter the value to be insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
push(value);
break;
case 2: pop();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nWrong selection!!! Try again!!!");
}
}
}
void push(int value){
if(top == SIZE-1)
printf("\\nStack is Full!!! Insertion is not possible!!!");
else{
top++;
stack[top] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion success!!!");
}
}
void pop(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack is Empty!!! Deletion is not possible!!!");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted : %d", stack[top]);
top--;
}
}
void display(){
if(top == -1)
printf("\\nStack is Empty!!!");
else{
int i;
printf("\\nStack elements are:\\n");
for(i=top; i>=0; i--)
printf("%d\\n",stack[i]);
}
}
E.g.

Queue
A Queue is an ordered collection of items from which items may be deleted at one end (called the front of the queue) and into which items may be inserted at the other end (the rear of the queue).
Queue follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) methodology, i.e. the first element inserted into the queue is the first element to be removed.
Implementation of Queue using array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define SIZE 10
void enQueue(int);
void deQueue();
void display();
int queue[SIZE], front = -1, rear = -1;
void main()
{
int value, choice;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n\\n***** MENU *****\\n");
printf("1. Insertion\\n2. Deletion\\n3. Display\\n4. Exit");
printf("\\nEnter your choice: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case 1: printf("Enter the value to be insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
enQueue(value);
break;
case 2: deQueue();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nWrong selection!!! Try again!!!");
}
}
}
void enQueue(int value){
if(rear == SIZE-1)
printf("\\nQueue is Full!!! Insertion is not possible!!!");
else{
if(front == -1)
front = 0;
rear++;
queue[rear] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion success!!!");
}
}
void deQueue(){
if(front == rear)
printf("\\nQueue is Empty!!! Deletion is not possible!!!");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted : %d", queue[front]);
front++;
if(front == rear)
front = rear = -1;
}
}
void display(){
if(rear == -1)
printf("\\nQueue is Empty!!!");
else{
int i;
printf("\\nQueue elements are:\\n");
for(i=front; i<=rear; i++)
printf("%d\\t",queue[i]);
}
}
E.g.
AI is thinking...
5. Evaluate the expression ABCD-x+ using stack where A=5, B=4, C=3 and D=7.
AI is thinking...
5. Transform the postfix expression AB − C + DEF − + $ to infix.
Given postfix expression:
AB − C + DEF − + $
Converting it into infix:
|
Characters |
Stack |
Operation |
|
A |
A |
|
|
B |
A, B |
|
|
- |
|
(A-B) |
|
|
(A-B) |
|
|
C |
(A-B), C |
|
|
+ |
|
((A-B)+C) |
|
|
((A-B)+C) |
|
|
D |
((A-B)+C), D |
|
|
E |
((A-B)+C), D, E |
|
|
F |
((A-B)+C), D, E,
F |
|
|
- |
((A-B)+C), D |
(E-F) |
|
|
((A-B)+C), D,
(E-F) |
|
|
+ |
((A-B)+C) |
(D-(E-F)) |
|
|
((A-B)+C), (D-(E-F)) |
|
|
$ |
|
(((A-B)+C)$ (D-(E-F))) |
|
|
(((A-B)+C)$ (D-(E-F))) |
|
The infix expression of given postfix
expression is: (((A-B)+C)$ (D-(E-F)))
AI is thinking...
5. Construct an expression tree from the following postfix:
AB + C*DC – -FG + $
Given postfix expression:
AB + C*DC – -FG + $
Expression tree for given expression is constructed below:
AI is thinking...
6. What is ADT? Discuss stack as an ADT.
Abstract data types are a set of data values and associated operations that are precisely independent of any particular implementation. Generally the associated operations are abstract methods. E.g. stack, queue etc.
Stack as an ADT
A stack of elements of type T is a finite sequence of elements of T together with the operations
- CreateEmptyStack(S): Create or make stack S be an empty stack
- Push(S, x): Insert x at one end of the stack, called its top
- Top(S): If stack S is not empty; then retrieve the element at its top
- Pop(S): If stack S is not empty; then delete the element at its top
- IsFull(S): Determine if S is full or not. Return true if S is full stack; return false otherwise
- IsEmpty(S): Determine if S is empty or not. Return true if S is an empty stack; return false otherwise.
Thus by using a stack we can perform above operations thus a stack acts as an ADT.
AI is thinking...
6. How can you convert from infix to post fix notation?
Algorithm to convert infix to postfix expression
1. Scan the infix string from left to right.
2. Initialize an empty stack.
3. If the scanned character is an operand, add it to postfix sting
4. If the scanned character is an operator, PUSH the character to stack.
5. If the top operator in stack has equal or higher precedence than scanned operator then POP the operator present in stack and add it to postfix string else PUSH the scanned character to stack.
6. If the scanned character is a left parenthesis ‘(‘, PUSH it to stack.
7. If the scanned character is a right parenthesis ‘)’, POP and add to postfix string from stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered. Ignore both '(' and ')'.
8. Repeat step 3-7 till all the characters are scanned.
9. After all character are scanned POP the characters and add to postfix string from the stack until it is not empty.
Example:
Infix expression: A*B+C
characters | stacks | Postfix expression |
A | A | |
* | * | A |
B | * | AB |
+ | + | AB* |
C | + | AB*C |
AB*C+ |
Postfix expression: AB*C+
AI is thinking...
6. Explain the infix to post fix conversion algorithm.
Algorithm to convert infix to postfix expression
1. Scan the infix string from left to right.
2. Initialize an empty stack.
3. If the scanned character is an operand, add it to postfix sting
4. If the scanned character is an operator, PUSH the character to stack.
5. If the top operator in stack has equal or higher precedence than scanned operator then POP the operator present in stack and add it to postfix string else PUSH the scanned character to stack.
6. If the scanned character is a left parenthesis ‘(‘, PUSH it to stack.
7. If the scanned character is a right parenthesis ‘)’, POP and add to postfix string from stack until an ‘(‘ is encountered. Ignore both '(' and ')'.
8. Repeat step 3-7 till all the characters are scanned.
9. After all character are scanned POP the characters and add to postfix string from the stack until it is not empty.
Example:
Infix expression: A*B+C
characters | stacks | Postfix expression |
A | A | |
* | * | A |
B | * | AB |
+ | + | AB* |
C | + | AB*C |
AB*C+ |
Postfix expression: AB*C+
AI is thinking...
7. How stack as ADT? Explain with example.
A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items may be inserted and from which items may be deleted at one end, called the top of the stack. The deletion and insertion in a stack is done from top of the stack.
It is a linear data structure which store data temporarily to perform PUSH and POP operation in LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) sequence.

Fig::A stack containing items or elements
Stack as ADT
A stack of elements of type T is a finite sequence of elements of T together with the operations
- CreateEmptyStack(S): Create or make stack S be an empty stack
- Push(S, x): Insert x at one end of the stack, called its top
- Top(S): If stack S is not empty; then retrieve the element at its top
- Pop(S): If stack S is not empty; then delete the element at its top
- IsFull(S): Determine if S is full or not. Return true if S is full stack; return false otherwise
- IsEmpty(S): Determine if S is empty or not. Return true if S is an empty stack; return false otherwise.
Thus by using a stack we can perform above operations thus a stack acts as an ADT.
AI is thinking...
1. Define queue. What are different applications of queue? Explain queue operations with example. (1+2+7)
AI is thinking...
1. Define Queue as an ADT. Write a program for basic operations in Linear queue in array implementation.
A Queue is an ordered collection of items from which items may be deleted at one end (called the front of the queue) and into which items may be inserted at the other end (the rear of the queue).
Queue follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) methodology, i.e. the first element inserted into the queue is the first element to be removed.
A queue q of type T is a finite sequence of elements with the operations:
- MakeEmpty(q): To make q as an empty queue
- IsEmpty(q): To check whether the queue q is empty. Return true if q is empty, return false otherwise.
- IsFull(q): To check whether the queue q is full. Return true in q is full, return false otherwise.
- Enqueue(q, x): To insert an item x at the rear of the queue, if and only if q is not full.
- Dequeue(q): To delete an item from the front of the queue q. if and only if q is not empty.
- Traverse (q): To read entire queue that is display the content of the queue.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define
SIZE 10
void
enQueue(int);
void
deQueue();
void
display();
int
queue[SIZE], front = -1, rear = -1;
void
main()
{
int value, choice;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n\\n***** MENU
*****\\n");
printf("1. Insertion\\n2.
Deletion\\n3. Display\\n4. Exit");
printf("\\nEnter your choice:
");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case
1: printf("Enter the value to be insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
enQueue(value);
break;
case 2: deQueue();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nWrong selection!!! Try
again!!!");
}
}
}
void
enQueue(int value){
if(rear == SIZE-1)
printf("\\nQueue is Full!!! Insertion
is not possible!!!");
else{
if(front == -1)
front = 0;
rear++;
queue[rear] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion
success!!!");
}
}
void
deQueue(){
if(front == rear)
printf("\\nQueue is Empty!!! Deletion
is not possible!!!");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted : %d",
queue[front]);
front++;
if(front == rear)
front = rear = -1;
}
}
void
display(){
if(rear == -1)
printf("\\nQueue is Empty!!!");
else{
int i;
printf("\\nQueue elements
are:\\n");
for(i=front; i<=rear; i++)
printf("%d\\t",queue[i]);
}
}
AI is thinking...
1. Define Queue as ADT. Describe its primitive operation on array implementation and linked list implementation.
A Queue is an ordered collection of items from which items may be deleted at one end (called the front of the queue) and into which items may be inserted at the other end (the rear of the queue).
Queue follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) methodology, i.e. the first element inserted into the queue is the first element to be removed.
A queue q of type T is a finite sequence of elements with the operations:
- MakeEmpty(q): To make q as an empty queue
- IsEmpty(q): To check whether the queue q is empty. Return true if q is empty, return false otherwise.
- IsFull(q): To check whether the queue q is full. Return true in q is full, return false otherwise.
- Enqueue(q, x): To insert an item x at the rear of the queue, if and only if q is not full.
- Dequeue(q): To delete an item from the front of the queue q. if and only if q is not empty.
- Traverse (q): To read entire queue that is display the content of the queue.
The operations that can be performed on the queue are as follows:
- MakeEmpty(q): To make q as an empty queue
- Enqueue(q, x): To insert an item x at the rear of the queue, this is also called by names add, insert.
- Dequeue(q): To delete an item from the front of the queue q. this is also known as Delete, Remove.
- IsFull(q): To check whether the queue q is full.
- IsEmpty(q): To check whether the queue q is empty
- Traverse (q): To read entire queue that is display the content of the queue.
E.g.
fig: Enqueue and Dequeue operations
AI is thinking...
3. What is circular queue? Write an algorithm and C function to implement Circular queue.
Circular Queue is a linear data
structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First
Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to
make a circle.
Graphical representation of a circular queue is as follows:
Initialization of
Circular queue:
rear=front=MAXSIZE-1
Algorithms for inserting an element in a circular queue:
This
algorithm is assume that rear and front are initially set to MAZSIZE-1.
1.
if (front==(rear+1)%MAXSIZE)
print Queue is full and exit
else
rear=(rear+1)%MAXSIZE; [increment rear by 1]
2.
cqueue[rear]=item;
3.
end
Algorithms for deleting an element from a circular queue:
This
algorithm is assume that rear and front are initially set to MAZSIZE-1.
1.
if (rear==front) [checking empty condition]
print Queue is empty and exit
2.
front=(front+1)%MAXSIZE; [increment front by 1]
3.
item=cqueue[front];
4.
return item;
5. end.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define
SIZE 5
void
enQueue(int);
void
deQueue();
void
display();
int
cQueue[SIZE], front = -1, rear = -1;
void
main()
{
int choice, value;
clrscr();
while(1){
printf("\\n****** MENU
******\\n");
printf("1. Insert\\n2. Delete\\n3.
Display\\n4. Exit\\n");
printf("Enter your choice: ");
scanf("%d",&choice);
switch(choice){
case 1: printf("\\nEnter the value to be
insert: ");
scanf("%d",&value);
enQueue(value);
break;
case 2: deQueue();
break;
case 3: display();
break;
case 4: exit(0);
default: printf("\\nPlease select the
correct choice!!!\\n");
}
}
}
void
enQueue(int value)
{
if((front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1)
|| (front == rear+1))
printf("\\nCircular Queue is Full!
Insertion not possible!!!\\n");
else{
if(rear == SIZE-1 && front != 0)
rear = -1;
cQueue[++rear] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion
Success!!!\\n");
if(front == -1)
front = 0;
}
}
void
deQueue()
{
if(front == -1 && rear == -1)
printf("\\nCircular Queue is Empty!
Deletion is not possible!!!\\n");
else{
printf("\\nDeleted element :
%d\\n",cQueue[front++]);
if(front == SIZE)
front = 0;
if(front-1 == rear)
front = rear = -1;
}
}
void
display()
{
if(front == -1)
printf("\\nCircular Queue is
Empty!!!\\n");
else{
int i = front;
printf("\\nCircular Queue Elements
are : \\n");
if(front <= rear){
while(i <= rear)
printf("%d\\t",cQueue[i++]);
}
else{
while(i <= SIZE - 1)
printf("%d\\t", cQueue[i++]);
i
= 0;
while(i <= rear)
printf("%d\\t",cQueue[i++]);
}
}
}
AI is thinking...
4. Write C function to insert an item circular queue in array implementation. Write assumptions, you need.
C function to insert an item circular queue in array implementation:
void
enQueue(int value)
{
if((front == 0 && rear == SIZE - 1)
|| (front == rear+1))
printf("\\nCircular Queue is Full!
Insertion not possible!!!\\n");
else{
if(rear == SIZE-1 && front != 0)
rear = -1;
cQueue[++rear] = value;
printf("\\nInsertion
Success!!!\\n");
if(front == -1)
front = 0;
}
}
AI is thinking...
6. What is priority queue? Why do we need this type of queue?
AI is thinking...
5. Compare stack with queue. How is linear queue different from circular queue?
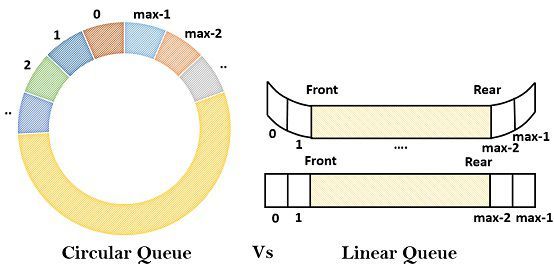
Comparison between stack and queue

Difference between linear queue and circular queue
1. The linear queue is an ordered list in which data elements are organized in the sequential order. In contrast, circular queue stores the data in the circular fashion.
2. Linear queue follows the FIFO order for executing the task (the element added in the first position is going to be deleted in the first position). Conversely, in the circular queue, the order of operations performed on an element may change.
3. The insertion and deletion of the elements is fixed in linear queue i.e. addition from the rear end and deletion from the front end. On the other hand, the circular queue is capable of inserting and deleting the element from any point until it is unoccupied.
4. Linear queue wastes the memory space while circular queue makes the efficient use of space.
AI is thinking...
6. Write C function to display all the items in a circular queue in array implementation. Write assumptions, you need.
void
display()
{
if(front == -1)
printf("\\nCircular Queue is
Empty!!!\\n");
else{
int i = front;
printf("\\nCircular Queue Elements
are : \\n");
if(front <= rear){
while(i <= rear)
printf("%d\\t",cQueue[i++]);
}
else{
while(i <= SIZE - 1)
printf("%d\\t", cQueue[i++]);
i
= 0;
while(i <= rear)
printf("%d\\t",cQueue[i++]);
}
}
}
AI is thinking...
7. How can you use Queue as ADT?
A Queue is an ordered collection of items from which items may be deleted at one end (called the front of the queue) and into which items may be inserted at the other end (the rear of the queue).
Queue follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) methodology, i.e. the first element inserted into the queue is the first element to be removed.
A queue q of type T is a finite sequence of elements with the operations:
- MakeEmpty(q): To make q as an empty queue
- IsEmpty(q): To check whether the queue q is empty. Return true if q is empty, return false otherwise.
- IsFull(q): To check whether the queue q is full. Return true in q is full, return false otherwise.
- Enqueue(q, x): To insert an item x at the rear of the queue, if and only if q is not full.
- Dequeue(q): To delete an item from the front of the queue q. if and only if q is not empty.
- Traverse (q): To read entire queue that is display the content of the queue.
AI is thinking...
7. Describe circular Queue operations in array implementation.
Circular Queue is a linear data
structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First
Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to
make a circle.
Graphical representation of a circular queue is as follows.
Initialization of Circular queue:
rear=front=MAXSIZE-1
Operations of Circular Queue
1. enQueue(value): This function is used to insert an element into the circular queue. In a circular queue, the new element is always inserted at Rear position.
Algorithms for inserting an element in a circular queue:
This
algorithm is assume that rear and front are initially set to MAZSIZE-1.
1.
if (front==(rear+1)%MAXSIZE)
print Queue is full and exit
else
rear=(rear+1)%MAXSIZE; [increment rear by 1]
2.
cqueue[rear]=item;
3. end
Algorithms for deleting an element from a circular queue:
This
algorithm is assume that rear and front are initially set to MAZSIZE-1.
1.
if (rear==front) [checking empty condition]
print Queue is empty and exit
2.
front=(front+1)%MAXSIZE; [increment front by 1]
3.
item=cqueue[front];
4.
return item;
5. end.
AI is thinking...
13. What is priority queue? How it is best implemented?
A
priority queue is a collection of elements such that each element has been assigned
a priority and the order in which elements are deleted and processed comes from
the following rules:.
- An element of higher priority is
processed before any element of lower priority.
- If two elements has same priority then they are processed according to the order in which they were added to the queue.
There are two types of priority
queues they are as follows...
- Max Priority Queue
- Min Priority Queue
1. Max Priority Queue: In max priority queue, elements are inserted in the order in which they arrive the queue and always maximum value is removed first from the queue. For example assume that we insert in order 8, 3, 2, 5 and they are removed in the order 8, 5, 3, 2.
2. Min Priority Queue: Min Priority Queue is similar to max priority queue except removing maximum element first, we remove minimum element first in min priority queue.
Priority Queues can be implemented using common data structures like arrays, linked-lists, heaps and binary trees.
AI is thinking...
2. Why recursion is required? Explain with Tower-of-Hanoi example. How recursive algorithm makes program effective? Write the merits and demerits of recursion in Programming.
Recursion is a process by which a function calls itself repeatedly, until some specified condition has been satisfied. The process is used for repetitive computations in which each action is stated in terms of a previous result.
Recursion is required because there are problems to solve which are recursive by nature. Non-recursive solutions to those problems are
- Complicated (because of the mismatch between the problem and the code) Fragile (be
- cause complicated)
- Harder to maintain and analyse (because of points 1 and 2)
- Potentially less efficient
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Example for 3 disks: 7 moves
Merits of recursion
1. The code may be easier to write.
2. To solve such problems which are naturally recursive such as tower of Hanoi.
3. Reduce unnecessary calling of function.
4. Extremely useful when applying the same solution.
5. Recursion reduce the length of code.
6. It is very useful in solving the data structure problem.
7. Stacks evolutions and infix, prefix, postfix evaluations etc.
Demerits of recursion
1. Recursive functions are generally slower than non-recursive function.
2. It may require a lot of memory space to hold intermediate results on the system stacks.
3. Hard to analyze or understand the code.
4. It is not more efficient in terms of space and time complexity.
5. The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not properly checked.
AI is thinking...
2. What do you mean by recursion? Explain the implementation of factorial and Fibonacci sequences with example.
Recursion is a process by which a function calls itself repeatedly, until some specified condition has been satisfied. The process is used for repetitive computations in which each action is stated in terms of a previous result.
In order to solve a problem recursively, two conditions must be satisfied. First, the problem must be written in a recursive form, and second, the problem statement must include a stopping condition.
C program to find factorial of an integer:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main( )
{
clrscr( );
int factorial(int);
int n,f;
printf("Enter the number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
f=factorial(n);
printf("Factorial of the %d number is %d",n,f);
getch();
}
int factorial(int n)
{
int f;
if(n==1)
return 1;
else
f=n*factorial(n-1);
return f;
}
E.g.
A Fibonacci sequence is the sequence of integer in which each element in the sequence is the sum of the two previous elements.
Fibonacci series starts from two numbers − F0 & F1. The initial values of F0 & F1 can be taken 0, 1 or 1, 1 respectively.
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
E.g.
F8 = 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 8, 13 or, F8 = 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
Program to generate Fibonacci series up to n terms
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int n, i;
int fibo(int);
printf("Enter n:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("Fibonacci numbers up to %d terms:\\n",n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d\\n",fibo(i));
getch();
}
int fibo(int k)
{
if(k == 0 || k == 1)
return k;
else
return fibo(k-1)+fibo(k-2);
}
AI is thinking...
4. What is Recursion? Write a recursive algorithm to implement binary search.
Recursion is a process by which a function calls itself repeatedly, until some specified condition has been satisfied. The process is used for repetitive computations in which each action is stated in terms of a previous result.
Recursive algorithm to implement binary search
int binarySearch(int A[], int low, int high, int x)
{
if (low > high) {
return -1;
}
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (x == A[mid]) {
return mid;
}
else if (x < A[mid]) {
return binarySearch(A, low, mid - 1, x);
}
else {
return binarySearch(A, mid + 1, high, x);
}
}
AI is thinking...
4. State TOH problem. Write recursion tree when no. of disks are four.
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Recursion Tree for TOH
1. Move Tower(N-1, BEG, END,AUX)
2. Move Tower(1, BEG, AUX, END) à(BEG à END)
3. Move Tower (N-1, AUX, BEG, END)
Recursion Tree when no. of disks are 4 as:
AI is thinking...
4. Consider the function:
Void transfer (int n, char from, char to, char temp)
{
if (n > 0)
{
transfer ( n – 1, from, temp, to);
Printf ( “Move Disk % d from % C to % C” N, from, to);
transfer ( n – 1, temp, to, from);
}
}
Trace the output with the function Call:
transfer ( 3, "R‟, "L‟, „"C‟);
Function call:
transfer ( 3, "R‟, "L‟, „"C‟);
Output:
Move Disk 1 from R to L
Move Disk 2 from R to C
Move Disk 1 from L to C
Move Disk 3 from R to L
Move Disk 1 from C to R
Move Disk 2 from C to L
Move Disk 1 from R to L
It can be shown in figure as:
AI is thinking...
4. Write recursive algorithm to get Fibonacci term. Illustrate it drawing recursion tree.
A Fibonacci sequence is the sequence of integer in which each element in the sequence is the sum of the two previous elements.
Fibonacci series starts from two numbers − F0 & F1. The initial values of F0 & F1 can be taken 0, 1 or 1, 1 respectively.
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
E.g.
F8 = 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 8, 13 or, F8 = 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
Recursive algorithm to get Fibonacci sequence:
1. START
2. Input the non-negative integer ‘n’
3. If (n==o || n==1)
return n;
else
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2);
4. Print, nth Fibonacci number
5. END
Recursion tree using algorithm Fibonacci with N=4 as:
AI is thinking...
7. Write recursive program to find nth fibonacci number.
AI is thinking...
6. What is recursion? Write a recursive program to find factorial of a number.
Recursion is a process by which a function calls itself repeatedly, until some specified condition has been satisfied. The process is used for repetitive computations in which each action is stated in terms of a previous result.
In order to solve a problem recursively, two conditions must be satisfied. First, the problem must be written in a recursive form, and second, the problem statement must include a stopping condition.
Recursive program to find factorial of a number:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main( )
{
clrscr( );
int factorial(int);
int n,f;
printf("Enter the number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
f=factorial(n);
printf("Factorial of the %d number is %d",n,f);
getch();
}
int factorial(int n)
{
int f;
if(n==1)
return 1;
else
f=n*factorial(n-1);
return f;
}
AI is thinking...
6. State TOH problem. Explain a recursive algorithm to solve the problem.
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Recursive solution:
void TOH(int n, char A, char B, char C)
{
if(n>0)
{
TOH(n-1, A, C, B);
Printf(“Move disk %d from %c to%c\\n”, n, A, B);
TOH(n-1, C, B, A);
}
}
AI is thinking...
7. Explain the Tower of Hanoi (TOH) with practical example.
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Example for 3 disks: 7 moves
AI is thinking...
7. Define recursive algorithm? How do you implement recursive algorithms while writing computer programs?
A recursive algorithm is an algorithm which calls itself with "smaller (or simpler)" input values, and which obtains the result for the current input by applying simple operations to the returned value for the smaller (or simpler) input.
We can use following steps to implement recursive algorithm:
- Initialize the algorithm. Recursive programs often need a seed value to start with. This is accomplished either by using a parameter passed to the function or by providing a gateway function that is nonrecursive but that sets up the seed values for the recursive calculation.
- Check to see whether the current value(s) being processed match the base case. If so, process and return the value.
- Redefine the answer in terms of a smaller or simpler sub-problem or sub-problems.
- Run the algorithm on the sub-problem.
- Combine the results in the formulation of the answer.
- Return the results.
For e.g.
Program to find factorial of an integer:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main( )
{
clrscr( );
int factorial(int);
int n,f;
printf("Enter the number: ");
scanf("%d",&n);
f=factorial(n);
printf("Factorial of the %d number is %d",n,f);
getch();
}
int factorial(int n)
{
int f;
if(n==1)
return 1;
else
f=n*factorial(n-1);
return f;
}
AI is thinking...
11. Write merits and demerits of recursive function over non-recursive function.
Merits of recursive function
1. The code may be easier to write.
2. To solve such problems which are naturally recursive such as tower of Hanoi.
3. Reduce unnecessary calling of function.
4. Extremely useful when applying the same solution.
5. Recursion reduce the length of code.
6. It is very useful in solving the data structure problem.
7. Stacks evolutions and infix, prefix, postfix evaluations etc.
Demerits of recursive function
1. Recursive functions are generally slower than non-recursive function.
2. It may require a lot of memory space to hold intermediate results on the system stacks.
3. Hard to analyze or understand the code.
4. It is not more efficient in terms of space and time complexity.
5. The computer may run out of memory if the recursive calls are not properly checked.
AI is thinking...
12. Write an algorithm to implement tower of Hanoi.
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Example for 3 disks: 7 moves
AI is thinking...
12. Explain the tower of Hanoi algorithm.
Tower of Hanoi (TOH) is a mathematical puzzle which consists of three pegs named as origin, intermediate and destination and more than one disks. These disks are of different sizes and the smaller one sits over the larger one.
In this problem we transfer all disks from origin peg to destination peg using intermediate peg for temporary storage and move only one disk at a time.
Algorithm for TOH problem:
Let’s consider move ‘n’ disks from source peg (A) to destination peg (C), using intermediate peg (B) as auxiliary.
1. Assign three pegs A, B & C
2. If n==1
Move the single disk from A to C and stop.
3. If n>1
a) Move the top (n-1) disks from A to B.
b) Move the remaining disks from A to C
c) Move the (n-1) disks from B to C
4. Terminate
Example for 3 disks: 7 moves
AI is thinking...
2. Explain circular linked list with example. How do you implement linked list operation in singly linked list? Explain. (4+6)
AI is thinking...
2. What do you mean by circular list? Differentiate between stack as a circular list and Queue as a circular list.
Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link to its next element in the sequence and the last element has a link to the first element in the sequence.
Circular linked lists can be used to help the traverse the same list again and again if needed. A circular list is very similar to the linear list where in the circular list the pointer of the last node points not NULL but the first node.
Example:
Circular list has no end.
Stack as a circular List
To implement a stack in a circular linked list, let pstack be a pointer to the last node of a circular list. Actually there is no any end of a list but for convention let us assume that the first node(rightmost node of a list) is the top of the stack.
An empty stack is represented by a null list.
The structure for the circular linked list implementation of stack is:
struct node
{
int info;
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node NodeType;
NodeType *pstack=NULL;
PUSH function:
void PUSH(int item)
{
NodeType newnode;
newnode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
newnode->info=item;
if(pstack==NULL)
{
pstack=newnode;
pstack->next=pstack;
}
else
{
newnode->next=pstack->next;
pstack->next=newnode;
}
}
POP function:
void POP()
{
NodeType *temp;
if(pstack==NULL)
{
printf(“Stack underflow\\n');
exit(1);
}
else if(pstack->next==pstack) //for only one node
{
printf(“poped item=%d”, pstack->info);
pstack=NULL;
}
else
{
temp=pstack->next;
pstack->next=temp->next;
printf(“poped item=%d”, temp->info);
free(temp);
}
}
Queue as a circular List
By using a circular list, a queue may be specified by a single pointer q to that list. node(q) is the rear of the queue and the following node is its front.
Insertion function:
void insert(int item)
{
NodeType *nnode;
nnode=( NodeType *)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
nnode->info=item;
if(pq==NULL)
pq=nnode;
else
{
nnode->next=pq->next;
pq->next=nnode;
pq=nnode;
}
}
Deletion function:
void delet(int item)
{
NodeType *temp;
if(pq==NULL)
{
printf(“void deletion\\n”);
exit(1);
}
else if(pq->next==pq)
{
printf(“poped item=%d”, pq->info);
pq=NULL;
}
else
{
temp=pq->next;
pq->next=temp->next;
printf(“poped item=%d”, temp->info);
free(temp);
}
}
AI is thinking...
2. State relative merits and demerits of contiguous list and Linked list. Explain the steps involved in inserting and deleting a node in singly linked list.
Merits of Contiguous List / array
• It is used to represent multiple data items of same type by using only single name.
• It can be used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs etc.
• 2D arrays are used to represent matrices.
• Implementation of list using array is easier as compared other implementation.
Demerits of Contiguous List / array
• The size of the array is fixed. Most often this size is specified at compile time. This makes the programmers to allocate arrays, which seems "large enough" than required.
• Inserting new elements at the front is potentially expensive because existing elements need to be shifted over to make room.
• Deleting an element from an array is not possible. Linked lists have their own strengths and weaknesses, but they happen to be strong where arrays are weak.
• Generally array's allocates the memory for all its elements in one block whereas linked lists use an entirely different strategy. Linked lists allocate memory for each element separately and only when necessary.
Merits of Linked List
1. Linked lists are dynamic data structures. i.e., they can grow or shrink during the execution of a program.
2. Linked lists have efficient memory utilization. Here, memory is not preallocated. Memory is allocated whenever it is required and it is de-allocated (removed) when it is no longer needed.
3. Insertion and Deletions are easier and efficient. Linked lists provide flexibility in inserting a data item at a specified position and deletion of the data item from the given position.
4. Many complex applications can be easily carried out with linked lists.
5. There is no need to define an initial size for a Linked list.
6. Linked List reduces the access time.
Demerits of Linked List
1. They use more memory than arrays because of the storage used by their pointers.
2. Difficulties arise in linked lists when it comes to reverse traversing. For instance, singly linked lists are cumbersome to navigate backwards and while doubly linked lists are somewhat easier to read, memory is wasted in allocating space for a back-pointer.
3. Nodes in a linked list must be read in order from the beginning as linked lists are inherently sequential access.
4. Nodes are stored in-contiguously, greatly increasing the time required to access individual elements within the list, especially with a CPU cache.
Singly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link to its next element in the sequence. For e.g. the following example is a singly linked list that contains three elements 12, 99, & 37.
Steps involved in inserting a node at the beginning of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to head
NewNode->next=head;
4. Set the head pointer to the new node
head=NewNode;
5. End
Steps involved in inserting a node at the end of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to NULL
NewNode->next=NULL;
4. if (head ==NULL)then
Set head =NewNode.and exit.
5. Set temp=head;
6 while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp=temp->next; //increment temp
7. Set temp->next=NewNode;
8. End
Steps involved in deleting the first node of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. If(head==NULL) then
print “Void deletion” and exit
2. Store the address of first node in a temporary variable temp.
temp=head;
3. Set head to next of head.
head=head->next;
4. Free the memory reserved by temp variable.
free(temp);
5. End
Steps involved in deleting the last node of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. If(head==NULL) then //if list is empty
print “Void deletion” and exit
2. else if(head->next==NULL) then //if list has only one node
Set temp=head;
print deleted item as,
printf(“%d” ,head->info);
head=NULL;
free(temp);
3. else
set temp=head;
while(temp->next->next!=NULL)
set temp=temp->next;
End of while
free(temp->next);
Set temp->next=NULL;
4. End
AI is thinking...
2. Explain the structure of Doubly Linked List (DLL). Differentiate the difference between DLL and Doubly Circular Linked List (DCLL). Explain the procedures to insert a node in DLL at the beginning and at the last.
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Example:
1.Allocate memory for the new node as,
newnode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType))
2. Assign value to info field of a new node
set newnode->info=item
3. set newnode->prev=newnode->next=NULL
4. set newnode->next=head
5. set head->prev=newnode
6. set head=newnode
7. End
Procedure for inserting a node at the end of a doubly linked list:
1. Allocate memory for the new node as,
newnode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType))
2. Assign value to info field of a new node
set newnode->info=item
3. set newnode->next=NULL
4. if head==NULL
set newnode->prev=NULL;
set head=newnode;
5. if head!=NULL
set temp=head
while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp=temp->next;
end while
set temp->next=newnode;
set newnode->prev=temp
6. End
AI is thinking...
2. What is linked list? Explain the process of inserting and removing nodes from a linked list.
A linked list is a non-sequential collection of data items (nodes). It is a dynamic data structure. For every data item in a linked list, there is an associated pointer that would give the memory location of the next data item in the linked list. The data items in the linked list are not in consecutive memory locations. They may be anywhere, but the accessing of these data items is easier as each data item contains the address of the next data item.
Each node (data item) consists of two parts:
• Info: the actual element to be stored in the list. It is also called data field.
• Link: one or two links that points to next and previous node in the list. It is also called next or pointer field.
info next
Steps involved in inserting a node at the beginning of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to head
NewNode->next=head;
4. Set the head pointer to the new node
head=NewNode;
5. End
Steps involved in inserting a node at the end of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to NULL
NewNode->next=NULL;
4. if (head ==NULL)then
Set head =NewNode.and exit.
5. Set temp=head;
6 while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp=temp->next; //increment temp
7. Set temp->next=NewNode;
8. End
Steps involved in deleting the first node of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. If(head==NULL) then
print “Void deletion” and exit
2. Store the address of first node in a temporary variable temp.
temp=head;
3. Set head to next of head.
head=head->next;
4. Free the memory reserved by temp variable.
free(temp);
5. End
Steps involved in deleting the last node of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. If(head==NULL) then //if list is empty
print “Void deletion” and exit
2. else if(head->next==NULL) then //if list has only one node
Set temp=head;
print deleted item as,
printf(“%d” ,head->info);
head=NULL;
free(temp);
3. else
set temp=head;
while(temp->next->next!=NULL)
set temp=temp->next;
End of while
free(temp->next);
Set temp->next=NULL;
4. End
AI is thinking...
6. Differentiate between contiguous list and linked list with examples.
Different between contiguous list (array) and linked list
Array (Contiguous List) | Linked list |
1. Array is a collection of elements having same data type with common name. 2. In array, elements are stored in consecutive manner in memory. 3. Insertion & deletion takes more time in array as elements are stored in consecutive memory locations. 4. In array, memory is allocated at compile time i.e. Static Memory Allocation. 5. Array can be single dimensional, two dimension or multidimensional. 6. In array, each element is independent, no connection with previous element or with its location. | 1. Linked list is an ordered collection of elements which are connected by links/pointers. 2. In linked list, elements can be stored at any available place as address of node is stored in previous node. 3. Insertion & deletion are fast & easy in linked list as only value of pointer is needed to change. 4. In linked list, memory is allocated at run time i.e. Dynamic Memory Allocation. 5. Linked list can be singly, doubly or circular linked list. 6. In Linked list, location or address of elements is stored in the link part of previous element/node |
AI is thinking...
6. Differentiate between Singly linked list, DLL, CLL and DCLL.
Singly Linked List
Singly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link to its next element in the sequence. In any single linked list, the individual element is called as "Node". Every "Node" contains two fields, data and next. The data field is used to store actual value of that node and next field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence.
In this type of linked list, only one link in each node, where the link points to the next node in the list. The link of last node has a NULL pointer.
The graphical representation of a node in a single linked list is as follows...
The following example is a singly linked list that contains three elements 12, 99, & 37.
Doubly Linked List (DLL)
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Example:
Circular Linked List (CLL)
Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link to its next element in the sequence and the last element has a link to the first element in the sequence.
Example:
Circular list has no end.
In a circular linked list there are two methods to know if a node is the first node or not.
- Either a external pointer, list, points the first node or
- A header node is placed as the first node of the circular list.
Doubly Circular Linked List (DCLL)
A circular doubly linked list is one which has the successor and predecessor pointer in circular manner. It is a doubly linked list where the next link of last node points to the first node and previous link of first node points to last node of the list. E.g.
AI is thinking...
8. Explain array implementation of lists.
AI is thinking...
8. What are the benefits of using linked list over array? How can you insert a node in a singly linked list?
Linked lists and arrays are similar since they both store collections of data. Array is the most common data structure used to store collections of elements. Arrays are convenient to declare and provide the easy syntax to access any element by its index number. Once the array is set up, access to any element is convenient and fast.
The benefits of using linked list over array are:
1. Linked lists are dynamic data structures. i.e., they can grow or shrink during the execution of a program.
2. Linked lists have efficient memory utilization. Here, memory is not preallocated. Memory is allocated whenever it is required and it is de-allocated (removed) when it is no longer needed.
3. Insertion and Deletions are easier and efficient. Linked lists provide flexibility in inserting a data item at a specified position and deletion of the data item from the given position.
4. Many complex applications can be easily carried out with linked lists.
5. There is no need to define an initial size for a Linked list.
6. Linked List reduces the access time.
Steps involved in inserting a node at the beginning of singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to head
NewNode->next=head;
4. Set the head pointer to the new node
head=NewNode;
5. End
Steps involved in inserting a node at the end of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to NULL
NewNode->next=NULL;
4. if (head ==NULL)then
Set head =NewNode.and exit.
5. Set temp=head;
6 while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp=temp->next; //increment temp
7. Set temp->next=NewNode;
8. End
AI is thinking...
8. Write an algorithm and C function to delete node in singly link list.
An algorithm to deleting the first node of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. Create a new node using malloc function
NewNode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
2. Assign data to the info field of new node
NewNode->info=newItem;
3. Set next of new node to head
NewNode->next=head;
4. Set the head pointer to the new node
head=NewNode;
5. End
C function:
void deleteBeg()
{
NodeType *temp;
if(head==NULL)
{
printf(“Empty list”);
exit(1).
}
else
{
temp=head;
printf(“Deleted item is %d” , head->info);
head=head->next;
free(temp);
}
}
An algorithm to deleting the last node of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list
1. If(head==NULL) then //if list is empty
print “Void deletion” and exit
2. else if(head->next==NULL) then //if list has only one node
Set temp=head;
print deleted item as,
printf(“%d” ,head->info);
head=NULL;
free(temp);
3. else
set temp=head;
while(temp->next->next!=NULL)
set temp=temp->next;
End of while
free(temp->next);
Set temp->next=NULL;
4. End
C Function:
void deleteEnd()
{
NodeType *temp;
if(head==NULL)
{
printf(“Empty list”);
return;
}
else if(head->next==NULL)
{
temp=head;
head=NULL;
printf(“Deleted item is %d”, temp->info);
free(temp);
}
else
{
temp=head;
while(temp->next->next!=NULL)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
printf(“deleted item is %d'” , temp->next->info):
free(temp->next);
temp->next=NULL;
}
}
AI is thinking...
8. What do you mean by double linked list? Explain with example.
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Example:
- In double linked list, the first node must be always pointed by head.
- Always the previous field of the first node must be NULL.
- Always the next field of the last node must be NULL
Representation of doubly linked list
struct node
{
int info;
struct node *prev;
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node NodeType;
NodeType *head=NULL:
AI is thinking...
8. How do you insert a nodes at last in doubly linked list? Explain.
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Steps to insert a nodes at last in doubly linked list
1. Allocate memory for the new node as,
newnode=(NodeType*)malloc(sizeof(NodeType))
2. Assign value to info field of a new node
set newnode->info=item
3. set newnode->next=NULL
4. if head==NULL
set newnode->prev=NULL;
set head=newnode;
5. if head!=NULL
set temp=head
while(temp->next!=NULL)
temp=temp->next;
end while
set temp->next=newnode;
set newnode->prev=temp
6. End
AI is thinking...
9. Explain why linked list is called dynamic list? Write the algorithm for deleting a new node before a node.
A linked list is called a dynamic list because it can be used with a data collection that grows and shrinks during program execution. The exact amount of memory space required by a program depends on the data being processed and so this requirement cannot be found in advance. Linked list uses runtime allocation of memory resulting in no wastage of memory space.
Algorithm for deleting the node at the specified position of the singly linked list:
let *head be the pointer to first node in the current list 1. Read position of a node which to be deleted, let it be pos. 2. if head==NULL print “void deletion” and exit 3. Enter position of a node at which you want to delete a new node. Let this position is pos. 4. Set temp=head declare a pointer of a structure let it be *p 5. if (head ==NULL)then print “void ideletion” and exit otherwise;. 6. for(i=1; i<pos-1; i++) temp=temp->next; 7. print deleted item is temp->next->info 8. Set p=temp->next; 9. Set temp->next =temp->next->next; 10. free(p); 11. End |
AI is thinking...
12. Explain CLL, DLL, DCLL (Circular, Doubly, Doubly Circular Linked List).
Circular Linked List (CLL)
Circular linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has link to its next element in the sequence and the last element has a link to the first element in the sequence.
Example:
Circular list has no end.
In a circular linked list there are two methods to know if a node is the first node or not.
- Either a external pointer, list, points the first node or
- A header node is placed as the first node of the circular list.
Doubly Linked List (DLL)
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Example:
Doubly Circular Linked List (DCLL)
A circular doubly linked list is one which has the successor and predecessor pointer in circular manner. It is a doubly linked list where the next link of last node points to the first node and previous link of first node points to last node of the list. E.g.
AI is thinking...
12. Discuss the merits and demerits of contiguous list and linked list.
Merits of Contiguous List / array
• It is used to represent multiple data items of same type by using only single name.
• It can be used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs etc.
• 2D arrays are used to represent matrices.
• Implementation of list using array is easier as compared other implementation.
Demerits of Contiguous List / array
• The size of the array is fixed. Most often this size is specified at compile time. This makes the programmers to allocate arrays, which seems "large enough" than required.
• Inserting new elements at the front is potentially expensive because existing elements need to be shifted over to make room.
• Deleting an element from an array is not possible. Linked lists have their own strengths and weaknesses, but they happen to be strong where arrays are weak.
• Generally array's allocates the memory for all its elements in one block whereas linked lists use an entirely different strategy. Linked lists allocate memory for each element separately and only when necessary.
Merits of Linked List
1. Linked lists are dynamic data structures. i.e., they can grow or shrink during the execution of a program.
2. Linked lists have efficient memory utilization. Here, memory is not preallocated. Memory is allocated whenever it is required and it is de-allocated (removed) when it is no longer needed.
3. Insertion and Deletions are easier and efficient. Linked lists provide flexibility in inserting a data item at a specified position and deletion of the data item from the given position.
4. Many complex applications can be easily carried out with linked lists.
5. There is no need to define an initial size for a Linked list.
6. Linked List reduces the access time.
Demerits of Linked List
1. They use more memory than arrays because of the storage used by their pointers.
2. Difficulties arise in linked lists when it comes to reverse traversing. For instance, singly linked lists are cumbersome to navigate backwards and while doubly linked lists are somewhat easier to read, memory is wasted in allocating space for a back-pointer.
3. Nodes in a linked list must be read in order from the beginning as linked lists are inherently sequential access.
4. Nodes are stored in-contiguously, greatly increasing the time required to access individual elements within the list, especially with a CPU cache.
AI is thinking...
13. Write short notes on (any two):
a) Queue in circular linked list
b) ADT
c) MST (Minimum Cost Spanning Tree) of a graph.
a) Queue in Circular Linked List
By using a circular list, a queue may be specified by a single pointer q to that list. node(q) is the rear of the queue and the following node is its front.
Insertion function:
void insert(int item)
{
NodeType *nnode;
nnode=( NodeType *)malloc(sizeof(NodeType));
nnode->info=item;
if(pq==NULL)
pq=nnode;
else
{
nnode->next=pq->next;
pq->next=nnode;
pq=nnode;
}
}
Deletion function:
void delet(int item)
{
NodeType *temp;
if(pq==NULL)
{
printf(“void deletion\\n”);
exit(1);
}
else if(pq->next==pq)
{
printf(“poped item=%d”, pq->info);
pq=NULL;
}
else
{
temp=pq->next;
pq->next=temp->next;
printf(“poped item=%d”, temp->info);
free(temp);
}
}
b) ADT
Abstract data types are a set of data values and associated operations that are precisely independent of any particular implementation. Generally the associated operations are abstract methods. E.g. stack, queue etc.
c) MST (Minimum Cost Spanning Tree) of a graph
A spanning tree is a subset of Graph G, which has all the vertices of G with minimum possible number of edges. Hence, a spanning tree does not have cycles and it cannot be disconnected.
In a weighted graph, a minimum spanning tree (MST) is a spanning tree that has minimum weight than all other spanning trees of the same graph.
There are three different algorithms to construct the minimum spanning tree:
- Prim’s algorithm: Grows the tree in stages. Selects an edge with lowest cost that can be added to the tree without forming cycle.
- Kruskal’s algorithm: In each stage select the edge in non-decreasing order of cost.
- Sollin’s algorithm: Select several edges at each stage.
AI is thinking...
13. State relative merits & demerits of contiguous list and linked list.
Merits of Contiguous List / array
• It is used to represent multiple data items of same type by using only single name.
• It can be used to implement other data structures like linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs etc.
• 2D arrays are used to represent matrices.
• Implementation of list using array is easier as compared other implementation.
Demerits of Contiguous List / array
• The size of the array is fixed. Most often this size is specified at compile time. This makes the programmers to allocate arrays, which seems "large enough" than required.
• Inserting new elements at the front is potentially expensive because existing elements need to be shifted over to make room.
• Deleting an element from an array is not possible. Linked lists have their own strengths and weaknesses, but they happen to be strong where arrays are weak.
• Generally array's allocates the memory for all its elements in one block whereas linked lists use an entirely different strategy. Linked lists allocate memory for each element separately and only when necessary.
Merits of Linked List
1. Linked lists are dynamic data structures. i.e., they can grow or shrink during the execution of a program.
2. Linked lists have efficient memory utilization. Here, memory is not preallocated. Memory is allocated whenever it is required and it is de-allocated (removed) when it is no longer needed.
3. Insertion and Deletions are easier and efficient. Linked lists provide flexibility in inserting a data item at a specified position and deletion of the data item from the given position.
4. Many complex applications can be easily carried out with linked lists.
5. There is no need to define an initial size for a Linked list.
6. Linked List reduces the access time.
Demerits of Linked List
1. They use more memory than arrays because of the storage used by their pointers.
2. Difficulties arise in linked lists when it comes to reverse traversing. For instance, singly linked lists are cumbersome to navigate backwards and while doubly linked lists are somewhat easier to read, memory is wasted in allocating space for a back-pointer.
3. Nodes in a linked list must be read in order from the beginning as linked lists are inherently sequential access.
4. Nodes are stored in-contiguously, greatly increasing the time required to access individual elements within the list, especially with a CPU cache.
AI is thinking...
2. Explain concept of divide and conquer algorithm. Hand test quick algorithm with array of numbers (78, 34, 21, 43, 7, 18, 9, 56, 38, 19). What is time complexity of quick sort algorithm?
Divide-and-conquer algorithm breaks a problem into subproblems that are similar to the original problem, recursively solves the subproblems, and finally combines the solutions to the subproblems to solve the original problem.
Divide and Conquer algorithm consists of the following three steps.
- Divide: Divide the original problem into a set of subproblems.
- Conquer: Solve every subproblem individually, recursively.
- Combine: Put together the solutions of the subproblems to get the solution to the whole problem.
Given array:
78, 34, 21, 43, 7, 18, 9, 56, 38, 19
Sorting using quick sort:
......
Algorithm for Quick sort
QuickSort(A, l, r)
{
if(l<r)
{
p = Partition(A,l,r);
QuickSort(A,l,p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1,r);
}
}
Partition(A, l, r)
{
x =l; y =r ; p = A[l];
while(x<y)
{
do {
x++;
}while(A[x] <= p);
do {
y--;
} while(A[y] >=p);
if(x<y)
swap(A[x],A[y]);
}
A[l] = A[y];
A[y] = p;
return y; //return position of pivot
}
Time Complexity:
Best Case: T(n) = O(nlogn)
Worst Case: T(n) = O(n2)
Average Case: T(n) = O(nlogn)
AI is thinking...
3. What are external and internal sorting? Explain partition strategies of Merge sort and Quick sort. Trace these sort algorithms for following data:
11 45 61 33 55 9 83 25
Sorting is the technique to arranging the items of list in any specific order which may be ascending or descending order.
Sort can be classified in two types:
1. Internal sort: This method uses only the primary memory during sorting process. All data items are held in main memory and no secondary memory is required in this sorting process. If all the data that is to be sorted can be accommodated at a time in memory is called internal sorting. For e.g. selection sort, insertion sort etc.
Limitation: They can only process relatively small lists due to memory constrains.
2. External sort: Sorting large amount of data requires external or secondary memory. This process uses external memory such as HDD, to store the data which is not fit into the main memory. So primary memory holds the currently being sorted data only. All external sorts are based on process of merging. Different parts of data are sorted separately and merging together. For e.g. merge sort
Quick Sort
In quick sort one of the array element is chosen as a pivot element. Then large array is partitioned into two sub arrays one on left side of pivot which holds values smaller than the pivot element and another array on right side of pivot which holds values greater than pivot the pivot value. This procedure of choosing pivot and partition the list is applied recursively until sub-arrays consisting of only one element.
Algorithm:
QuickSort(A, l, r)
{
if(l<r)
{
p = Partition(A,l,r);
QuickSort(A,l,p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1,r);
}
}
Partition(A, l, r)
{
x =l; y =r ; p = A[l];
while(x<y)
{
do {
x++;
}while(A[x] <= p);
do {
y--;
} while(A[y] >=p);
if(x<y)
swap(A[x],A[y]);
}
A[l] = A[y];
A[y] = p;
return y; //return position of pivot
}
Merge Sort
The basic concept of merge sort is divides the list into two smaller sub-lists of approximately equal size. Recursively repeat this procedure till only one element is left in the sub-list. After this, various sorted sub-lists are merged to form sorted parent list. This process goes on recursively till the original sorted list arrived.
Algorithm:
MergeSort(A, l, r)
{
If ( l < r)
{
m = (l + r)/2
MergeSort(A, l, m)
MergeSort(A, m + 1, r)
Merge(A, l, m+1, r)
}
}
Merge(A, B, l, m, r)
{
x=l, y=m;
k=l;
while(x<m && y<r)
{
if(A[x] < A[y])
{
B[k]= A[x];
k++;
x++;
}
else
{
B[k] = A[y];
k++;
y++;
}
AI is thinking...
5. Write a program in C for bubble sorting.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10],i,j,temp,n;
printf("\\n Enter the max no.of Elements to Sort: \\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\\n Enter the Elements : \\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<n-i-1; j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}
printf("The sorted array is: \\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("%d\\t",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
AI is thinking...
6. Compare partition strategies of Merge sort and Quick sort.
Quick Sort
In quick sort one of the array element is chosen as a pivot element. Then large array is partitioned into two sub arrays one on left side of pivot which holds values smaller than the pivot element and another array on right side of pivot which holds values greater than pivot the pivot value. This procedure of choosing pivot and partition the list is applied recursively until sub-arrays consisting of only one element.
Algorithm:
QuickSort(A, l, r)
{
if(l<r)
{
p = Partition(A,l,r);
QuickSort(A,l,p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1,r);
}
}
Partition(A, l, r)
{
x =l; y =r ; p = A[l];
while(x<y)
{
do {
x++;
}while(A[x] <= p);
do {
y--;
} while(A[y] >=p);
if(x<y)
swap(A[x],A[y]);
}
A[l] = A[y];
A[y] = p;
return y; //return position of pivot
}
Merge Sort
The basic concept of merge sort is divides the list into two smaller sub-lists of approximately equal size. Recursively repeat this procedure till only one element is left in the sub-list. After this, various sorted sub-lists are merged to form sorted parent list. This process goes on recursively till the original sorted list arrived.
Algorithm:
MergeSort(A, l, r)
{
If ( l < r)
{
m = (l + r)/2
MergeSort(A, l, m)
MergeSort(A, m + 1, r)
Merge(A, l, m+1, r)
}
}
Merge(A, B, l, m, r)
{
x=l, y=m;
k=l;
while(x<m && y<r)
{
if(A[x] < A[y])
{
B[k]= A[x];
k++;
x++;
}
else
{
B[k] = A[y];
k++;
y++;
}
AI is thinking...
7. Explain Divide and Conquer algorithm taking reference to Merge Sort.
Divide-and-conquer algorithm breaks a problem into subproblems that are similar to the original problem, recursively solves the subproblems, and finally combines the solutions to the subproblems to solve the original problem.
Divide and Conquer algorithm consists of the following three steps.
- Divide: Divide the original problem into a set of subproblems.
- Conquer: Solve every subproblem individually, recursively.
- Combine: Put together the solutions of the subproblems to get the solution to the whole problem.

Merge sort works on the basis of divide and conquer algorithm. The basic concept of merge sort is divides the list into two smaller sub-lists of approximately equal size. Recursively repeat this procedure till only one element is left in the sub-list. After this, various sorted sub-lists are merged to form sorted parent list. This process goes on recursively till the original sorted list arrived.
Procedure for Merge sort:
To sort A[l…………r]
1. Divide step: If a given array A has zero or one element, simply return; it is already sorted. Otherwise split A[l……….r] into two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] each containing about half of the element A[l…….r]. that is q is the half of way point of A[l…….r].
2. Conquer step: Sorting the two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] recursively. When the size of sequence of is 1 there is nothing more to do.
3. Combine step: Combine the two sub-arrays A[l……q] and A[q+1…………r] into a sorted sequence.
AI is thinking...
7. Trace selection – sort algorithm for the following data:
42, 23, 74, 11, 65, 58, 94, 86
Selection sort algorithm sorts the elements in an array by finding the minimum element in each pass from unsorted part and keeps it in the beginning. This sorting technique maintains two sub arrays, one sub array which is already sorted and the other one which is unsorted. In each iteration the minimum element (ascending order) is picked from unsorted array and moved to sorted sub array.
Given data:
42, 23, 74, 11, 65, 58, 94, 86
Tracing using selection sort;
Which is the sorted array.
AI is thinking...
7. Explain Bubble sort algorithm. Illustrate it with an example.
Bubble sort algorithm arranges values by iterating over the list several times and in each iteration the larger value gets bubble up to the end of the list. This algorithm uses multiple passes and in each pass the first and second data items are compared. if the first data item is bigger than the second, then the two items are swapped. Next the items in second and third position are compared and if the first one is larger than the second, then they are swapped, otherwise no change in their order. This process continues for each successive pair of data items until all items are sorted.
Algorithm for Bubble Sort
Let a[n] be an array list of size n.
void bubbleSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
{
if( a[j] > a[j+1])
{
// swap the elements
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
Example:
Consider the array list:
5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 8 |
Source: w3resource.com
AI is thinking...
9. Hand test selection sort with array of numbers 4, 71, 32, 19, 61, 2, -5 in descending order.
AI is thinking...
8. Write a program to sort an array using selection sort.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10],i,j,temp,min,loc,n;
printf("\\n Enter the max no.of Elements to Sort: \\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\\n Enter the Elements : \\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
for (i=0; i<=n-1; i++)
{
min=a[i];
loc=i;
for (j=i+1; j<=n-1; j++)
{
if (a[j]<min)
{
min=a[j];
loc=j;
}
}
if (loc!=i)
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[loc];
a[loc]=temp;
}
}
printf("The sorted array is: \\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf("%d\\t",a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
AI is thinking...
9. What is sorting? Describe the Insertion sort.
Sorting is the technique to arranging the items of list in any specific order which may be ascending or descending order.
Insertion Sort
An algorithm consider the elements one at a time, inserting each in its suitable place among those already considered (keeping them sorted). Insertion sort is an example of an incremental algorithm. It builds the sorted sequence one number at a time.
Suppose a[0], a[1], a[2], …………….,a[n-1] are n elements in memory, insertion sort works as follow:
Pass 1: a[0] by itself is trivially sorted.
Pass 2: a[1] is inserted either before or after a[0] so that a[0], a[1] is sorted.
Pass 3: a[2] is inserted into its proper place in a[0],a[1], that is before a[0], between a[0] and a[1], or after a[1], so that: a[0],a[1], a[2] is sorted.
……
Pass n: a[n-1] is inserted into its proper place in a[0], a[1], a[2], ……….a[n-2] so that a[0], a[1], a[2], ……….a[n-1] is sorted array with ‘n’ elements.
Algorithm for Insertion Sort:
Let a[n] be an array of size n.
Void insertionsort(int a[], int a)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
temp= a[i];
j=j--;
while((temp<a[j])&&(j>=0))
{
a[j+1]= a[j];
j= j--;
}
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
Example:
A list of unsorted elements are: 9, 7, 6, 15, 16, 5, 10, 11
AI is thinking...
9. Write an algorithm and C function for merge sort.
The basic concept of merge sort is divides the list into two smaller sub-lists of approximately equal size. Recursively repeat this procedure till only one element is left in the sub-list. After this, various sorted sub-lists are merged to form sorted parent list. This process goes on recursively till the original sorted list arrived.
Procedure
To sort A[l………….r]
1. Divide step: If a given array A has zero or one element, simply return; it is already sorted. Otherwise split A[l……….r] into two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] each containing about half of the element A[l…….r]. that is q is the half of way point of A[l…….r].
2. Conquer step: Sorting the two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] recursively. When the size of sequence of is 1 there is nothing more to do.
3. Combine step: combine the two sub-arrays A[l……q] and A[q+1…………r] into a sorted sequence.
C function
MergeSort(A, l, r)
{
If ( l < r)
{
m = (l + r)/2
MergeSort(A, l, m)
MergeSort(A, m + 1, r)
Merge(A, l, m+1, r)
}
}
Merge(A, B, l, m, r)
{
x=l, y=m;
k=l;
while(x<m && y<r)
{
if(A[x] < A[y])
{
B[k]= A[x];
k++;
x++;
}
else
{
B[k] = A[y];
k++;
y++;
}
AI is thinking...
12. Write short notes on: (2 x 2.5 = 5)
a) Divide and conquer sorting
b) AVL tree
AI is thinking...
11. Differentiate between selection sort and bubble sort.
Bubble Sort:
This sorting technique is also known as exchange sort, which arranges values by iterating over the list several times and in each iteration the larger value gets bubble up to the end of the list. This algorithm uses multiple passes and in each pass the first and second data items are compared. if the first data item is bigger than the second, then the two items are swapped. Next the items in second and third position are compared and if the first one is larger than the second, then they are swapped, otherwise no change in their order. This process continues for each successive pair of data items until all items are sorted.
AI is thinking...
11. What do you mean by sorting? Explain the Bubble sort with example.
Sorting is the technique to arranging the items of list in any specific
order which may be ascending or descending order.
Bubble sort algorithm arranges values by iterating over the list several times and in each iteration the larger value gets bubble up to the end of the list. This algorithm uses multiple passes and in each pass the first and second data items are compared. if the first data item is bigger than the second, then the two items are swapped. Next the items in second and third position are compared and if the first one is larger than the second, then they are swapped, otherwise no change in their order. This process continues for each successive pair of data items until all items are sorted.
Algorithm for Bubble Sort
Let a[n] be an array list of size n.
void bubbleSort(int a[], int n)
{
int i, j, temp;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++)
{
if( a[j] > a[j+1])
{
// swap the elements
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
Example:
Consider the array list:
5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 8 |
Source: w3resource.com
AI is thinking...
12. Hand test the insertion sort algorithm with following array of numbers.
16 7 31 2 9 41 -10
Given array:
16 7 31 2 9 41 -10
Tracing using insertion sort:
Which is the sorted array.
AI is thinking...
13. Discuss merge sort. How you rate this sorting from selection sort?
The basic concept of merge sort is divides the list into two smaller sub-lists of approximately equal size. Recursively repeat this procedure till only one element is left in the sub-list. After this, various sorted sub-lists are merged to form sorted parent list. This process goes on recursively till the original sorted list arrived.
Procedure
To sort A[l………….r]
1. Divide step: If a given array A has zero or one element, simply return; it is already sorted. Otherwise split A[l……….r] into two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] each containing about half of the element A[l…….r]. that is q is the half of way point of A[l…….r].
2. Conquer step: Sorting the two sub-arrays A[l………q] and A[q+1…………r] recursively. When the size of sequence of is 1 there is nothing more to do.
3. Combine step: combine the two sub-arrays A[l……q] and A[q+1…………r] into a sorted sequence.
C function
MergeSort(A, l, r)
{
If ( l < r)
{
m = (l + r)/2
MergeSort(A, l, m)
MergeSort(A, m + 1, r)
Merge(A, l, m+1, r)
}
}
Merge(A, B, l, m, r)
{
x=l, y=m;
k=l;
while(x<m && y<r)
{
if(A[x] < A[y])
{
B[k]= A[x];
k++;
x++;
}
else
{
B[k] = A[y];
k++;
y++;
}
AI is thinking...
7. Explain binary search. Illustrate it with example.
Binary
search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item
in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements.
The logic behind the technique is:
1. First
find the middle element of the list
2. Compare
the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If
it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
Algorithm:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Example:
Consider an array of data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for above data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
S.No. | L | R | Mid=(L+R)/2 | Remarks |
1. 2. | 0 4 | 7 7 | (0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 | Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123) is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
AI is thinking...
8. Trace Binary Search algorithm for the data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
And Search for the values 123 and 153.
Given:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for given data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
|
S.No. |
L |
R |
Mid=(L+R)/2 |
Remarks |
|
1. 2. |
0 4 |
7 7 |
(0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 |
Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123)
is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
Again,
L=0, R=14, key=153 (search for 153)
|
S.No. |
L |
R |
Mid=(L+R)/2 |
Remarks |
|
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. |
0 4 6 7 7 |
7 7 7 7 6 |
(0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 (6+7)/3=6 (7+7)/2=7 - |
Key>a[3] Key>a[5] Key>a[6] Key<a[7] L>R |
Therefore, search failure and key(153) is not present in the given list.
AI is thinking...
10. Write a program to implement sequential search algorithm.
AI is thinking...
8. Compare and Contrast between Binary searching and Binary tree searching.
AI is thinking...
8. What is Hashing? What collision means? State collision resolution techniques. Explain one of them in brief.
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
Collision
The situation in which the hash function returns the same hash key for more than one record is called collision. For e.g.
Consider a hash function:
H(key) = recordkey%10 having the hash table size of 10
The record keys to be placed are: 131, 44, 43, 78, 19, 36, 57 and 77
131%10= 1
44%10=4
43%10=3
78%10=8
19%10=9
36%10=6
57%10=7
77%10=7
Now if we try to place 77 in the hash table then we get the hash key to be 7 and at index 7 already the record key 57 is placed. This situation is called collision.
Collision resolution techniques
If collision occurs then it should be handled by applying some techniques. Such a technique is called collision handling technique. Some collision resolution techniques are:
1.Chaining
2.Open addressing (linear probing)
3.Quadratic probing
4.Double hashing
5.Rehashing
Chaining:
In collision handling method chaining is a concept which introduces an additional field with data i.e. chain. A separate chain table is maintained for colliding data. When collision occurs then a linked list(chain) is maintained at the key. For e.g.
Consider the keys to be placed in their hash key are 131, 3, 4, 21, 61, 7, 97, 8, 9 then we will apply a hash function as
H(key) = key % D Where D is the size of table. The hash table will be:
Here D = 10
A chain is maintained for colliding elements. for instance 131 has a home bucket (key) 1.
similarly key 21 and 61 demand for home bucket 1. Hence a chain is maintained at index 1.
AI is thinking...
8. Explain hashing with example.
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
E.g. Division Hash Function
The division hash function depends upon the remainder of division. Typically the divisor is table length. For e.g. If the record 54, 72, 89, 37 is placed in the hash table and if the table size is 10 then the hash function is:
h(key) = record % table size
and key obtained by hash function is called hash key.
54%10=4
72%10=2
89%10=9
37%10=7
AI is thinking...
9. How do you implement binary search algorithm? What is time complexity of this algorithm?
Binary search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements. The logic behind the technique is:
1. First find the middle element of the list
2. Compare the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
Recursive Algorithm:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Example:
Consider an array of data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for above data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
S.No. | L | R | Mid=(L+R)/2 | Remarks |
1. 2. | 0 4 | 7 7 | (0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 | Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123) is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
Efficiency:
From the above algorithm we can say that the running time of the algorithm is
T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1)
= O(logn)
In the best case output is obtained at one run i.e. O(1) time if the key is at middle.
In the worst case the output is at the end of the array so running time is O(logn) time. In the average case also running time is O(logn).
AI is thinking...
9. Describe recursive procedure of Binary searching technique? Discuss about efficiency of Binary searching.
Binary search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements. The logic behind the technique is:
1. First find the middle element of the list
2. Compare the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
Recursive Algorithm:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Example:
Consider an array of data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for above data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
S.No. | L | R | Mid=(L+R)/2 | Remarks |
1. 2. | 0 4 | 7 7 | (0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 | Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123) is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
Efficiency:
From
the above algorithm we can say that the running time of the algorithm is
T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1)
= O(logn)
In
the best case output is obtained at one run i.e. O(1)
time if the key is at middle.
In
the worst case the output is at the end of the array so running time is O(logn) time. In the average case also running time is O(logn).
AI is thinking...
9. Discuss binary search technique along with its efficiency.
Binary search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements. The logic behind the technique is:
1. First find the middle element of the list
2. Compare the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
Recursive Algorithm:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Example:
Consider an array of data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for above data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
S.No. | L | R | Mid=(L+R)/2 | Remarks |
1. 2. | 0 4 | 7 7 | (0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 | Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123) is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
Efficiency:
From the above algorithm we can say that the running time of the algorithm is
T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1)
= O(logn)
In the best case output is obtained at one run i.e. O(1) time if the key is at middle.
In the worst case the output is at the end of the array so running time is O(logn) time. In the average case also running time is O(logn).
AI is thinking...
9. State collision resolution techniques in hashing. Explain double hashing and quadratic probing techniques.
Collision resolution techniques
If collision occurs then it should be handled by applying some techniques. Such a technique is called collision handling technique. Collision resolution techniques are:
1.Chaining
2.Open addressing (linear probing)
3.Quadratic probing
4.Double hashing
5.Rehashing
Quadratic Probing:
Quadratic probing operates by taking the original hash value and adding successive values of an arbitrary quadratic polynomial to the starting value. This method uses following formula:
where m can be table size or any prime number
For e.g. If we have to insert following elements in the hash table with table size 10:
37, 90, 55, 22, 11, 17
37 % 10 = 7
90 % 10 = 0
55 % 10 = 5
22 % 10 = 2
11 % 10 = 1
Now if we want to place 17 a collision will occur as 17%10 = 7 and bucket 7 has already an element 37. Hence we will apply quadratic probing to insert this record in the hash table.
Consider i = 0 then
(17 + 0
2
) % 10 = 7
(17 + 12 ) % 10 = 8, when i =1
The bucket 8 is empty hence we will place the element at index 8.
Double Hashing
Double hashing is technique in which a second hash function is applied to the key when a collision occurs. By applying the second hash function we will get the number of positions from the point of collision to insert. There are two important rules to be followed for the second function:
it must never evaluate to zero.
must make sure that all cells can be probed.
The formula to be used for double hashing is
where M is a prime number smaller than the size of the table.
Consider the following elements to be placed in the hash table of size 10
37, 90, 45, 22, 17
Initially insert the elements using the formula for H1(key).
Insert 37, 90, 45, 22
H1(37) = 37 % 10 = 7
H1(90) = 90 % 10 = 0
H1(45) = 45 % 10 = 5
H1(22) = 22 % 10 = 2
H1(49) = 49 % 10 = 9
Now if 17 to be inserted then
Here M is prime number smaller than the size of the table. Prime number smaller than table size 10 is 7
Hence M = 7
That means we have to insert the element 17 at 4 places from 37. In short we have to take 4 jumps. Therefore the 17 will be placed at index 1.
AI is thinking...
10. Why do we need Hashing? Discuss linear probing in detail.
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
In a hash table, data is stored in an array format, where each data value has its own unique index value. Access of data becomes very fast if we know the index of the desired data. Thus, using hashing insertion and search operations are very fast irrespective of the size of the data. So we need hashing.
Linear Probing
Linear probing is the method of handling collision. When collision occurs i.e. when two records demand for the same home bucket in the hash table then collision can be solved by placing the second record linearly down whenever the empty bucket is found. When use linear probing, the hash table is represented as a one-dimensional array with indices that range from 0 to the desired table size-1. Before inserting any elements into this table, we must initialize the table to represent the situation where all slots are empty. This allows us to detect overflows and collisions when we inset elements into the table. Then using some suitable hash function the element can be inserted into the hash table.
For example:
Consider that following keys are to be inserted in the hash table
131, 4, 8, 7, 21, 5, 31, 61, 9, 29
Initially, we will put the following keys in the hash table.
We will use Division hash function. That means the keys are placed using the formula
H(key) = key % tablesize
H(key) = key % 10
For instance the element 131 can be placed at
H(key) = 131 % 10 = 1
Index 1 will be the home bucket for 131. Continuing in this fashion we will place 4, 8, 7.
Now the next key to be inserted is 21. According to the hash function
H(key)=21%10 = 1
But the index 1 location is already occupied by 131 i.e. collision occurs. To resolve this collision we will linearly move down and at the next empty location we will prob the element. Therefore 21 will be placed at the index 2.
AI is thinking...
10. What is hashing? Discuss rehashing with example.
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
E.g. Division Hash Function
The division hash function depends upon the remainder of division. Typically the divisor is table length. For e.g. If the record 54, 72, 89, 37 is placed in the hash table and if the table size is 10 then the hash function is:
h(key) = record % table size
and key obtained by hash function is called hash key.
54%10=4
72%10=2
89%10=9
37%10=7
Rehashing
Rehashing is a collision resolution technique.
Rehashing is a technique in which the table is resized, i.e., the size of table is doubled by creating a new table. It is preferable is the total size of table is a prime number. There are situations in which the rehashing is required.
• When table is completely full
• With quadratic probing when the table is filled half.
• When insertions fail due to overflow.
In such situations, we have to transfer entries from old table to the new table by re computing their positions using hash functions.
Consider we have to insert the elements 37, 90, 55, 22, 17, 49, and 87. the table size is 10 and will use hash function:
H(key) = key mod tablesize
37 % 10 = 7
90 % 10= 0
55 % 10 = 5
22 % 10 = 2
17 % 10 = 7
49 % 10 = 9
Now this table is almost full and if we try to insert more elements collisions will occur and eventually further insertions will fail. Hence we will rehash by doubling the table size. The old table size is 10 then we should double this size for new table, that becomes 20. But 20 is not a prime number, we will prefer to make the table size as 23. And new hash function will be
H(key) key mod 23
37 % 23 = 14
90 % 23 = 21
55 % 23 = 9
22 % 23 = 22
17 % 23 = 17
49 % 23 = 3
87 % 23 = 18
Now the hash table is sufficiently large to accommodate new insertions.
AI is thinking...
10. Explain the binary searching.
Binary search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements. The logic behind the technique is:
1. First find the middle element of the list
2. Compare the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
Recursive Algorithm:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Example:
Consider an array of data:
21, 36, 56, 79, 101, 123, 142, 203
Now,
Tracing binary search for above data;
Set L=0, R=7, key=123 (search for 123)
S.No. | L | R | Mid=(L+R)/2 | Remarks |
1. 2. | 0 4 | 7 7 | (0+7)/2=3 (4+7)/2=5 | Key>a[3] Key==a[5] |
Therefore, search successful and key(123) is at position (Mid+1)=5+1=6.
AI is thinking...
10. What are Hashing and collision? Write about any three hashing algorithms.
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
Collision
The situation in which the hash function returns the same hash key for more than one record is called collision. For e.g.
Consider a hash function:
H(key) = recordkey%10 having the hash table size of 10
The record keys to be placed are: 131, 44, 43, 78, 19, 36, 57 and 77
131%10= 1
44%10=4
43%10=3
78%10=8
19%10=9
36%10=6
57%10=7
77%10=7
Now if we try to place 77 in the hash table then we get the hash key to be 7 and at index 7 already the record key 57 is placed. This situation is called collision.
Hashing algorithms/ Functions
1. Division Hash Function:
The division hash function depends upon the remainder of division. Typically the divisor is table length. For e.g. If the record 54, 72, 89, 37 is placed in the hash table and if the table size is 10 then the hash function is:
h(key) = record % table size
and key obtained by hash function is called hash key.
54%10=4
72%10=2
89%10=9
37%10=7
2. Mid Square Hash Function:
In the mid square method, the key is squared and the middle or mid part of the result is used as the index. If the key is a string, it has to be preprocessed to produce a number.
Consider that if we want to place a record 3111 then
31112 = 9678321
for the hash table of size 1000
H(3111) = 783 (the middle 3 digits)
3. Multiplicative Hash Function:
The given record is multiplied by some constant value. The formula for computing the hash key is
H(key) = floor(p *(fractional part of key*A)) where p is integer constant and A is constant real number.
Donald Knuth suggested to use constant A = 0.61803398987
If key 107 and p=50 then
H(key) = floor(50*(107*0.61803398987))
= floor(3306.4818458045)
= 3306
At 3306 location in the hash table the record 107 will be placed
AI is thinking...
12. Differentiate between sequential searching and binary searching.
Sequential Search
In this technique, we access each element of list one by one sequentially and see whether it is desired element or not. i.e. the key element is compared with the first element of the list, if the match is found, then search is successful and return the position of key. Otherwise next element of the list is compared with key and this process is continued till the key is found or list is completely searched.
Algorithm:
LinearSearch(A, n,key)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(A[i] == key)
return i;
}
return -1; //-1 indicates unsuccessful search
}
Binary search is an extremely efficient search technique that searches the given item in minimum possible comparisons in the already sorted list of given elements. The logic behind the technique is:
1. First find the middle element of the list
2. Compare the mid-element with searched item.
There are three cases:
a. If it is a desired element then search is successful.
b. If it is less than desired item then search only in the first half of the list.
c. If it is greater than desired item then search in the second half of the list.
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
AI is thinking...
12. Explain efficiency of
a) Binary Searching
b) Quick sort
a) Binary Searching
Algorithm for Binary Searching:
BinarySearch(A,l,r, key)
{
if(l= = r)
{
if(key = = A[l])
return l+1; //index starts from 0
else
return 0;
}
else
{
m = (l + r) /2 ;
if(key = = A[m])
return m+1;
else if (key < A[m])
return BinarySearch(l, m-1, key) ;
else
return BinarySearch(m+1, r, key) ;
}
}
Efficiency:
From the above algorithm we can say that the running time of the algorithm is
T(n) = T(n/2) + O(1)
= O(logn)
In the best case output is obtained at one run i.e. O(1) time if the key is at middle.
In the worst case the output is at the end of the array so running time is O(logn) time. In the average case also running time is O(logn).
b) Quick Sort
Algorithm for Quick Sort:
QuickSort(A, l, r)
{
if(l<r)
{
p = Partition(A,l,r);
QuickSort(A,l,p-1);
QuickSort(A,p+1,r);
}
}
Partition(A, l, r)
{
x =l; y =r ; p = A[l];
while(x<y)
{
do {
x++;
}while(A[x] <= p);
do {
y--;
} while(A[y] >=p);
if(x<y)
swap(A[x],A[y]);
}
A[l] = A[y];
A[y] = p;
return y; //return position of pivot
}
Efficiency:
Time Complexity:
Best Case: T(n) = O(nlogn)
Worst Case: T(n) = O(n2)
Average Case: T(n) = O(nlogn)
AI is thinking...
13. Write Short notes on (any two):
a) Hash function
b) External Sorting
c) ADT.
a) Hash Function
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
b) External Sorting
Sorting large amount of data requires external or secondary memory. This process uses external memory such as HDD, to store the data which is not fit into the main memory. So primary memory holds the currently being sorted data only. All external sorts are based on process of merging. Different parts of data are sorted separately and merging together. For e.g. merge sort
c) ADT
Abstract data types are a set of data values and associated operations that are precisely independent of any particular implementation. Generally the associated operations are abstract methods. E.g. stack, queue etc.
AI is thinking...
13. Write short notes on
a) Hashing
b) Doubly Linked list
a) Hashing
Hashing is a well-known technique to search any particular element among several elements. It minimizes the number of comparisons while performing the search.
In hashing, an array data structure called as Hash table is used to store the data items. Hash table is a data structure used for storing and retrieving data very quickly. Insertion of data in the hash table is based on the key value. Hence every entry in the hash table is associated with some key. Using the hash key the required piece of data can be searched in the hash table by few or more key comparisons.
Fig: Hashing Mechanism
Hash function is a function which is used to put the data in the hash table. Hence one can use the same hash function to retrieve the data from the hash table. Thus hash function is used to implement the hash table. The integer returned by the hash function is called hash key.
E.g. Division Hash Function
The division hash function depends upon the remainder of division. Typically the divisor is table length. For e.g. If the record 54, 72, 89, 37 is placed in the hash table and if the table size is 10 then the hash function is:
h(key) = record % table size
and key obtained by hash function is called hash key.
54%10=4
72%10=2
89%10=9
37%10=7
b) Doubly Linked List
Doubly linked list is a sequence of elements in which every element has links to its previous element and next element in the sequence.
In double linked list, every node has link to its previous node and next node. So, we can traverse forward by using next field and can traverse backward by using previous field. Every node in a double linked list contains three fields and they are shown in the following figure...
Here, 'link1' field is used to store the address of the previous node in the sequence, 'link2' field is used to store the address of the next node in the sequence and 'data' field is used to store the actual value of that node.
Example:
AI is thinking...
1. What do you mean by binary tree? Explain the binary search tree with example.
A binary tree is a finite set of elements that are either empty or is partitioned into three disjoint subsets.
- The first subset contains a single element called the root of the tree.
- The other two subsets are themselves binary trees called the left and right sub-trees of the original tree.
Each element of a binary tree is called a node of the tree.
The following figure shows a binary tree with 9 nodes where A is the root.
Binary Search Tree
A
binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree that is either empty or in which
every node contains a key (value) and satisfies the following conditions:
- All keys in the left sub-tree of the root are smaller than
the key in the root node
- All keys in the right sub-tree of the root are greater than
the key in the root node
- The left and right sub-trees of the root are again binary
search trees
Example:
Given the following sequence of numbers,
14,
4, 15, 3, 9, 14, 18
The following binary search tree can be constructed:
Following operations can be done in Binary Search Tree (BST):
- Search(k, T): Search for key k in the tree T. If k is found in some node of tree then return true otherwise return false.
- Insert(k, T): Insert a new node with value k in the info field in the tree T such that the property of BST is maintained.
- Delete(k, T):Delete a node with value k in the info field from the tree T such that the property of BST is maintained.
- FindMin(T), FindMax(T): Find minimum and maximum element from the given nonempty BST.
AI is thinking...
1. What is binary search tree? Explain with an example. Write an algorithm to search, insert and delete node in binary search tree.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree that is either empty or in which every node contains a key (value) and satisfies the following conditions:
- All keys in the left sub-tree of the root are smaller than the key in the root node
- All keys in the right sub-tree of the root are greater than the key in the root node
- The left and right sub-trees of the root are again binary search trees
Example:
Given the following sequence of numbers,
14, 4, 15, 3, 9, 14, 18
The following binary search tree can be constructed:
Algorithm to search the element in BST
void BinSearch(struct bnode *root , int key)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
printf(“The number does not exist”);
exit(1);
}
else if (key == root->info)
{
printf(“The searched item is found”):
}
else if(key < root->info)
return BinSearch(root->left, key);
else
return BinSearch(root->right, key);
}
Algorithm to insert the element in BST
void insert(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
if(root=NULL)
{
root=(struct bnode*)malloc (sizeof(struct bnode));
root->left=root->right=NULL;
root->info=item;
}
else
{
if(item<root->info)
root->left=insert(root->left, item);
else
root->right=insert(root->right, item);
}
}
Algorithm to delete the element in BST
struct bnode *delete(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
struct bnode *temp;
if(root==NULL)
{
printf(“Empty tree”);
return;
}
else if(item<root->info)
root->left=delete(root->left, item);
else if(item>root->info)
root->right=delete(root->right, item);
else if(root->left!=NULL &&root->right!=NULL) //node has two child
{
temp=find_min(root->right);
root->info=temp->info;
root->right=delete(root->right, root->info);
}
else
{
temp=root;
if(root->left==NULL)
root=root->right;
else if(root->right==NULL)
root=root->left;
free(temp);
}
return(temp);
}
Finding minimum element function:
struct bnode *find_min(struct bnode *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return0;
else if(root->left==NULL)
return root;
else
return(find_min(root->left));
}
AI is thinking...
1. Illustrate the algorithm for Binary search tree with example.
Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree that is either empty or in which every node contains a key (value) and satisfies the following conditions:
- All keys in the left sub-tree of the root are smaller than the key in the root node
- All keys in the right sub-tree of the root are greater than the key in the root node
- The left and right sub-trees of the root are again binary search trees
Example:
Given the following sequence of numbers,
14, 4, 15, 3, 9, 14, 18
The following binary search tree can be constructed:
Algorithm to search the element in BST
void BinSearch(struct bnode *root , int key)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
printf(“The number does not exist”);
exit(1);
}
else if (key == root->info)
{
printf(“The searched item is found”):
}
else if(key < root->info)
return BinSearch(root->left, key);
else
return BinSearch(root->right, key);
}
Algorithm to insert the element in BST
void insert(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
if(root=NULL)
{
root=(struct bnode*)malloc (sizeof(struct bnode));
root->left=root->right=NULL;
root->info=item;
}
else
{
if(item<root->info)
root->left=insert(root->left, item);
else
root->right=insert(root->right, item);
}
}
E.g.
Algorithm to delete the element in BST
struct bnode *delete(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
struct bnode *temp;
if(root==NULL)
{
printf(“Empty tree”);
return;
}
else if(item<root->info)
root->left=delete(root->left, item);
else if(item>root->info)
root->right=delete(root->right, item);
else if(root->left!=NULL &&root->right!=NULL) //node has two child
{
temp=find_min(root->right);
root->info=temp->info;
root->right=delete(root->right, root->info);
}
else
{
temp=root;
if(root->left==NULL)
root=root->right;
else if(root->right==NULL)
root=root->left;
free(temp);
}
return(temp);
}
Finding minimum element function:
struct bnode *find_min(struct bnode *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return0;
else if(root->left==NULL)
return root;
else
return(find_min(root->left));
}
E.g.
1. Deleting leaf Node
2. Deleting node with right child
3. Deleting node with left child
4. Deleting a node having both right and left child
AI is thinking...
2. Describe properties of Binary Search Tree. Write recursive algorithms for constructing BST and its traversals. Illustrate them with an example.
Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree that is either empty or in which every node contains a key (value) and satisfies the following conditions:
- All keys in the left sub-tree of the root are smaller than the key in the root node
- All keys in the right sub-tree of the root are greater than the key in the root node
- The left and right sub-trees of the root are again binary search trees
Example:
Given the following sequence of numbers,
14, 4, 15, 3, 9, 14, 18
The following binary search tree can be constructed:
Properties of BST:
- Nodes of the tree are represented in a parent-child relationship
- Each parent node can have zero child nodes or a maximum of two subnodes or subtrees on the left and right sides.
- Every sub-tree, also known as a binary search tree, has sub-branches on the right and left of themselves.
- All the nodes are linked with key-value pairs.
- The keys of the nodes present on the left subtree are smaller than the keys of their parent node
- Similarly, The left subtree nodes' keys have lesser values than their parent node's keys.
Recursive Algorithm for Constructing BST
void insert(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
if(root=NULL)
{
root=(struct bnode*)malloc (sizeof(struct bnode));
root->left=root->right=NULL;
root->info=item;
}
else
{
if(item<root->info)
root->left=insert(root->left, item);
else
root->right=insert(root->right, item);
}
}
Recursive Algorithm to traverse BST using preorder traverse method
void preorder(struct bnode *root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
printf(“%c”, root->info);
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
}
AI is thinking...
2. Describe the significance of Huffman tree. Describe procedure for construction of a Huffman tree. Illustrate it with example. Describe different types of applications of Binary trees.
Huffman
Coding is a technique of compressing data to reduce its size without losing any
of the details. It is generally useful to compress the data in which there
are frequently occurring characters.
Using
the Huffman tree, we can compress the string to a smaller size.
Procedure
for construction of Huffman tree
1.
Calculate the frequency of each character in the string.
2.
Sort the characters in increasing order of the frequency. These are stored in a
priority queue Q.
3.
Make each unique character as a leaf node.
4.
Create an empty node z. Assign the minimum frequency to the left
child of z and assign the second minimum frequency to the
right child of z. Set the value of the z as the
sum of the above two minimum frequencies.
5.
Remove these two minimum frequencies from Q and add the sum
into the list of frequencies.
6.
Insert node z into the tree.
7. Repeat
steps 3 to 5 for all the characters.
8. For each non-leaf node, assign 0 to the left edge and 1 to the right edge.
Example:
Let us take any four characters and their frequencies:
Now sort these characters according to their frequencies in non-decreasing order.
Here before using Huffman algorithm the total number of bits
required is
= 2*(6+3+2+1) = 24 bits.
The tree constructed for the above example is shown below:
Now from variable length code we get following code sequence.
Thus after using Huffman algorithm the total number of bits
required is
=1*3+2*3+3*2+6*1=21 bits
Applications of Binary trees
1. Binary Search Tree - Used in many search applications where data is constantly entering/leaving, such as the map and set objects in many languages' libraries.
2. Binary Space Partition - Used in almost every 3D video game to determine what objects need to be rendered.
3. Binary Tries - Used in almost every high-bandwidth router for storing router-tables.
4. Hash Trees - used in p2p programs and specialized image-signatures in which a hash needs to be verified, but the whole file is not available.
5. Heaps - Used in implementing efficient priority-queues, which in turn are used for scheduling processes in many operating systems, Quality-of-Service in routers, and A* (path-finding algorithm used in AI applications, including robotics and video games). Also used in heap-sort.
6. Huffman Coding Tree - Used in compression algorithms, such as those used by the .jpeg and .mp3 file-formats. GGM Trees - Used in cryptographic applications to generate a tree of pseudo-random numbers.
7. Syntax Tree - Constructed by compilers and (implicitly) calculators to parse expressions.
8. Treap - Randomized data structure used in wireless networking and memory allocation.
9. T-tree - Though most databases use some form of B-tree to store data on the drive, databases which keep all (most) their data in memory often use T-trees to do so.
AI is thinking...
3. What is binary search tree? Write a program to implement insertion and deletion algorithm in binary search tree? (2+8)
AI is thinking...
3. Discuss depth first and breadth first traversal of a graph with suitable example.
Traversing a graph means visiting all the vertices in a graph exactly one. In graph all nodes are treated equally. So the starting nodes in graph can be chosen arbitrarily.
A graph traversal finds the edges to be used in the search process without creating loops that means using graph traversal we visit all vertices of graph without getting into looping path.
Breadth First Search Traversal (BFS)
The traversal starts at a node v, after marking the node the traversal visits all incident edges to node v after marking the nodes and then moving to an adjacent node and repeating the process. The traversal continues until all unmarked nodes in the graph has been visited. A queue is maintained in the technique to maintain the list of incident edges and marked nodes.
Algorithm:
BFS(G,s) /* s is
start vertex */
{
T = {s};
L =Φ; /* an empty
queue */
Enqueue(L,s);
while (L != Φ )
{
v = dequeue(L);
for each neighbor w
to v
if ( wÏ L and w Ï T )
{
enqueue( L,w);
T = T U {w}; /* put
edge {v,w} also */
}
}
}
Example:
Choose a as initial vertex then we have
Order the vertices of level 1 i.e. {b, c, g, e, f}. Say order be {e, f, g, b, c}.
Depth First Traversal (DFS)
This technique picks up a node and marks it. An unmarked adjacent node to previous node is then selected and marked, become the new start node, possibly leaving the previous node with unexplored edges for the present. The traversal continued recursively, until all unmarked nodes of the current path are visited. The process is continued for all the paths of the graph. If this cannot be done, move back to another vertex and repeat the process. The whole process is continued until all the vertices are met. This method of search is also called backtracking. A stack data structure is maintained in the technique to maintain the list of incident edges and marked nodes.
Algorithm:
DFS(G,s)
{
T = {s};
Traverse(s);
}
Traverse(v)
{
for each w adjacent to v and not yet in T
{
T = T ∪ {w}; //put edge {v, w} also
Traverse (w);
}
}
Example:
Choose a as initial vertex then we have
AI is thinking...
3. Define Binary Search Tree (BST). Write an algorithm to insert a node in non-empty BST. Construct BST from the data:
10, 20, 30, 25, 27, 7, 4, 23, 26, 21.
Binary Search Tree
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree that is either empty or in which every node contains a key (value) and satisfies the following conditions:
- All keys in the left sub-tree of the root are smaller than the key in the root node
- All keys in the right sub-tree of the root are greater than the key in the root node
- The left and right sub-trees of the root are again binary search trees
Example:
Given the following sequence of numbers,
14, 4, 15, 3, 9, 14, 18
The following binary search tree can be constructed:
Algorithm to insert node in non-empty BST
Create a Node with given value and set its left and right to NULL.
insert(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
if(item < root->info)
root->left = insert(root->left, item);
else
root->right = insert(root->right, item);
return root;
}
E.g.
Given data
10, 20, 30, 25, 27, 7, 4, 23, 26, 21
Binary Search Tree (BST) for given data is given below:
AI is thinking...
3. Explain the procedure for construction of Huffman algorithm with example.
Huffman algorithm is a technique of compressing data to reduce its size without losing any of the details. It is generally useful to compress the data in which there are frequently occurring characters.
Using the Huffman tree, we can compress the string to a smaller size.
Procedure for construction of Huffman tree
1. Calculate the frequency of each character in the string.
2. Sort the characters in increasing order of the frequency. These are stored in a priority queue Q.
3. Make each unique character as a leaf node.
4. Create an empty node z. Assign the minimum frequency to the left child of z and assign the second minimum frequency to the right child of z. Set the value of the z as the sum of the above two minimum frequencies.
5. Remove these two minimum frequencies from Q and add the sum into the list of frequencies.
6. Insert node z into the tree.
7. Repeat steps 3 to 5 for all the characters.
8. For each non-leaf node, assign 0 to the left edge and 1 to the right edge.
Example:
Let us take any four characters and their frequencies:
Now sort these characters according to their frequencies in non-decreasing order.
Here before using Huffman algorithm the total number of bits required is
= 2*(6+3+2+1) = 24 bits.
The tree constructed for the above example is shown below:
Now from variable length code we get following code sequence.
Thus after using Huffman algorithm the total number of bits required is
=1*3+2*3+3*2+6*1=21 bits
AI is thinking...
3. A binary tree T has 12 nodes. The in-order and pre-order traversals of T yield the following sequence of nodes:
In-order : VPNAQRSOKBTM
Pre-order : SPVQNARTOKBM
Construct the Binary tree T showing each step. Explain, how you can arrive at solution in brief?
Given,
In-order : VPNAQRSOKBTM
Pre-order : SPVQNARTOKBM
In a Preorder sequence, leftmost element is the root of the tree. So we know ‘S’ is root for given sequences. By searching ‘S’ in In-order sequence, we can find out all elements on left side of ‘S’ are in left subtree and elements on right are in right subtree. So we know below structure now.
Among VPNAQR, P appears first in pre-order so it is root of left subtree.
Now, we recursively follow above steps for left subtree:
_______________
Among OKBTM, T appears first in pre-order so it is root of right subtree.
Now, we recursively follow above steps for right subtree:
_______________
Which is the required binary tree.
AI is thinking...
3. What is graph traversal? Discuss depth-first traversal technique with suitable example.
Traversing a graph means visiting all the vertices in a graph exactly one. In graph all nodes are treated equally. So the starting nodes in graph can be chosen arbitrarily.
A graph traversal finds the edges to be used in the search process without creating loops that means using graph traversal we visit all vertices of graph without getting into looping path.
Depth First Traversal (DFS)
This technique picks up a node and marks it. An unmarked adjacent node to previous node is then selected and marked, become the new start node, possibly leaving the previous node with unexplored edges for the present. The traversal continued recursively, until all unmarked nodes of the current path are visited. The process is continued for all the paths of the graph. If this cannot be done, move back to another vertex and repeat the process. The whole process is continued until all the vertices are met. This method of search is also called backtracking. A stack data structure is maintained in the technique to maintain the list of incident edges and marked nodes.
Algorithm:
DFS(G,s)
{
T = {s};
Traverse(s);
}
Traverse(v)
{
for each w adjacent to v and not yet in T
{
T = T ∪ {w}; //put edge {v, w} also
Traverse (w);
}
}
Example:
Choose a as initial vertex then we have
AI is thinking...
4. Explain Kruskal’s algorithm with example.
Kruskal's Algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph. The main target of the algorithm is to find the subset of edges by using which, we can traverse every vertex of the graph.
The Kruskal's algorithm is given as follows:
1. List all the edges of G with non-decreasing order of their weights.
2. Select an edge of minimum weight. This will be the first edge of T.
3. At each stage, select an edge of minimum weights from all remaining edges of G if it doesn’t form a cycle with previously selected edges in T. Then add the edge to T.
4. Repeat step 3 until n-1 edges have been selected.
(1, 6) | (4, 3) | (2, 7) | (2, 3) | (7, 4) | (4, 5) | (5, 7) | (5, 6) | (1, 2) |
7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 18 |
Pick edge (1, 6): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (4,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,7): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (7,4): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (4,5): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (5,7): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (5,6): No cycle is formed, include it.
Since the number of edges included equals (n– 1), the algorithm stops here.
AI is thinking...
5. Write about applications of Binary trees.
A binary tree is a finite set of elements that are either empty or is partitioned into three disjoint subsets.
- The first subset contains a single element called the root of the tree.
- The other two subsets are themselves binary trees called the left and right sub-trees of the original tree.
Each element of a binary tree is called a node of the tree.
The following figure shows a binary tree with 9 nodes where A is the root.
Applications of Binary Trees
1. Binary Search Tree - Used in many search applications where data is constantly entering/leaving, such as the map and set objects in many languages' libraries.
2. Binary Space Partition - Used in almost every 3D video game to determine what objects need to be rendered.
3. Binary Tries - Used in almost every high-bandwidth router for storing router-tables.
4. Hash Trees - used in p2p programs and specialized image-signatures in which a hash needs to be verified, but the whole file is not available.
5. Heaps - Used in implementing efficient priority-queues, which in turn are used for scheduling processes in many operating systems, Quality-of-Service in routers, and A* (path-finding algorithm used in AI applications, including robotics and video games). Also used in heap-sort.
6. Huffman Coding Tree - Used in compression algorithms, such as those used by the .jpeg and .mp3 file-formats. GGM Trees - Used in cryptographic applications to generate a tree of pseudo-random numbers.
7. Syntax Tree - Constructed by compilers and (implicitly) calculators to parse expressions.
8. Treap - Randomized data structure used in wireless networking and memory allocation.
9. T-tree - Though most databases use some form of B-tree to store data on the drive, databases which keep all (most) their data in memory often use T-trees to do so.
AI is thinking...
7. Explain almost complete binary tree with example.
A almost complete
binary tree is a binary tree in which every level of the tree is
completely filled except the last level. Also, in the last level, nodes should
be attached starting from the left-most position.
A binary tree is a almost complete binary tree (of height h , we
take root node as 0 ) if and only if :-
- Level 0 to h-1 represent a full binary tree of height h-1
- One or more nodes in level h-1 may have 0, or 1 child nodes
- If F, G are nodes in level h-1, then F has more child nodes than G if and only if F is to the left of G , i.e. the last level (h) can be missing leaf nodes, however the ones present must be shifted to the left
Example:
Fig: almost complete binary tree
AI is thinking...
8. What is Post-order traversal?
Post-order traversal is one of the multiple methods to traverse a tree.
In
Post-Order traversal, the root node is visited after left child and right
child. In this traversal, left child node is visited first, then its right
child and then its root node. This is recursively performed until the right
most node is visited.
Algorithm:
|
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Recursively traverse left
sub-tree. Step 2: Recursively traverse right
sub-tree. Step 3: Visit root node |
E.g.
The post-order traversal output of the given above tree is: H I D E B F G C A
C function for
post-order traversing:
Let pRoot is a given pointer to a root node of a binary tree.
void
post-order(BiNodeType *pRoot)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
postorder(pRoot->left);
postorder(pRoot->right);
printf(“%d”,
pRoot->info);
}
}
AI is thinking...
9. What is weighted graph? Explain Depth-first traversal of a graph.
Weighted Graph
A weighted graph is a graph G, in which each edge, e, is assigned a non-negative real number, w(e), called the weight of e. For e.g.
Depth First Traversal (DFS)
Depth-first traversal (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing graph data structures.
This technique picks up a node and marks it. An unmarked adjacent node to previous node is then selected and marked, become the new start node, possibly leaving the previous node with unexplored edges for the present. The traversal continued recursively, until all unmarked nodes of the current path are visited. The process is continued for all the paths of the graph. If this cannot be done, move back to another vertex and repeat the process. The whole process is continued until all the vertices are met. This method of search is also called backtracking. A stack data structure is maintained in the technique to maintain the list of incident edges and marked nodes.
Algorithm:
DFS(G,s)
{
T = {s};
Traverse(s);
}
Traverse(v)
{
for each w adjacent to v and not yet in T
{
T = T ∪ {w}; //put edge {v, w} also
Traverse (w);
}
}
Example:
Choose a as initial vertex then we have
AI is thinking...
9. What are the types of binary tree? Compare between them.
A binary tree is a finite set of elements that are either empty or is partitioned into three disjoint subsets.
- The first subset contains a single element called the root of the tree.
- The other two subsets are themselves binary trees called the left and right sub-trees of the original tree.
Each element of a binary tree is called a node of the tree.
A
binary tree in which every internal nodes has exactly two children and all leaf
nodes are at same level is called complete binary tree.
In complete binary tree:
- Tree of depth ‘d’ contains 2d nodes at level d.
- Depth of d of a binary tree will have 2d+1-1 nodes (total nodes).
- Depth of d will have 2d leaves and 2d-1non-leaf nodes (internal nodes).
- No. of external nodes=No. of internal nodes+1.
E.g.
2. Strictly binary tree
A
binary tree in which every node has either two or zero number of children is
called strictly binary tree.
- In
this tree every non-leaf node in a binary tree has nonempty left and right
sub-trees.
- A strictly binary tree with n leaves always contains 2n-1 nodes.
E.g.
3. Almost complete binary tree
A almost complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level of the tree is completely filled except the last level. Also, in the last level, nodes should be attached starting from the left-most position.
A binary tree is a almost complete binary tree (of height h , we take root node as 0 ) if and only if :-
- Level 0 to h-1 represent a full binary tree of height h-1
- One or more nodes in level h-1 may have 0, or 1 child nodes
- If F, G are nodes in level h-1, then F has more child nodes than G if and only if F is to the left of G , i.e. the last level (h) can be missing leaf nodes, however the ones present must be shifted to the left
E.g.
AI is thinking...
11. What is graph traversal? Explain.
AI is thinking...
9. Differentiate between tree and graph. What are spanning forest and spanning tree. Explain MST (Minimum cost Spanning Tree) problem.
Difference between tree and graph
Spanning Tree
A spanning tree is a subset of Graph G, which has all the vertices covered with minimum possible number of edges. Hence, a spanning tree does not have cycles and it cannot be disconnected.

Spanning Forest
Spanning forest is a forest that contains every vertex of G such that two vertices are in the same tree of the forest when there is a path in G between these two vertices.
--> Spanning forest is a forest of spanning tree in the sub-graph of G.
MST (Minimum cost Spanning Tree) problem
A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a spanning tree that has minimum weight than all other spanning trees of the same graph.
There are three different algorithms to construct the minimum spanning tree:
- Prim’s algorithm: Grows the tree in stages. Selects an edge with lowest cost that can be added to the tree without forming cycle.
- Kruskal’s algorithm: In each stage select the edge in non-decreasing order of cost.
- Sollin’s algorithm: Select several edges at each stage.
AI is thinking...
10. What do you mean by graph traversal? Explain prim's algorithm with example.
Traversing a graph means visiting all the vertices in a graph exactly one. In graph all nodes are treated equally. So the starting nodes in graph can be chosen arbitrarily.
A graph traversal finds the edges to be used in the search process without creating loops that means using graph traversal we visit all vertices of graph without getting into looping path.
Prim’s Algorithm
Prim's Algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree from a graph. Prim's algorithm finds the subset of edges that includes every vertex of the graph such that the sum of the weights of the edges can be minimized.
This algorithm involves the
following steps:
1. Select any vertex in G. Among all the edges which are
incident to it, choose an edge of minimum weight. Include it in T.
2. At each stage, choose an edge of smallest weight joining
a vertex which is already included in T and a vertex which is not included yet
so that it does not form a cycle. Then included it in T.
3. Repeat until all the vertices of G are included with n-1 edges.
Pseudocode:
T = ∅;
U = { 1 };
while (U ≠ V)
let (u, v) be the lowest cost edge such that u ∈ U and v ∈ V - U;
T = T ∪ {(u, v)}
U = U ∪ {v}AI is thinking...
10. Differentiate between pre-order traversal and in order traversal.
Pre-order Traversal
In Pre-Order traversal, the root node is visited before left child and right child nodes. In this traversal, the root node is visited first, then its left child and later its right child. This pre-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree.
Algorithm:
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Visit root node Step 2: Recursively traverse left sub-tree. Step 3: Recursively traverse right sub-tree. |
.
E.g.
The preorder traversal output of the given above tree is: A B D H I E C F G
In-order Traversal:
In In-Order traversal, the root node is visited between left child and right child. In this traversal, the left child node is visited first, then the root node is visited and later we go for visiting right child node. This in-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree. This is performed recursively for all nodes in the tree
Algorithm:
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Recursively traverse left sub-tree. Step 2: Visit root node Step 3: Recursively traverse right sub-tree. |
E.g.
The inorder traversal output of the given tree is: H D I B E A F C G
AI is thinking...
10. Create a Huffman tree for the following set of data:
Given,
Now sort these characters according to their frequencies in non-decreasing order.
The tree constructed for the given characters is shown below:
Now from variable length code we get following code sequence.
AI is thinking...
10. A file contains 100 symbols in which following character with their probability of occurrence. Build a Huff man tree according to Greedy Strategy.
Given character and their frequencies:
Now sort these characters according to their frequencies in non-decreasing order.
The Huffman tree constructed for the above data is shown below:
Now from variable length code we get following code sequence.
Thus after using Huffman algorithm the total number of bits required is
= 48*1+11*3+9*4+14*3+7*4+11*3= 220 bits
AI is thinking...
10. Explain the characteristics of Huffman’s algorithm and its application.
AI is thinking...
10. State MST (Minimum Cost Spanning Tree) problem and shortest path (single source and all other destination) problem. Name the algorithms for solving these problems.
MST (Minimum Cost Spanning Tree)
A
spanning tree is a subset of Graph G, which has all the vertices of G with
minimum possible number of edges. Hence, a spanning tree does not have cycles
and it cannot be disconnected.
In a
weighted graph, a minimum spanning tree (MST) is a spanning tree that
has minimum weight than all other spanning trees of the same graph.
There
are three different algorithms to construct the minimum spanning tree:
- Prim’s algorithm: Grows the tree
in stages. Selects an edge with lowest cost that can be added to the tree
without forming cycle.
- Kruskal’s algorithm: In each stage select the edge in non-decreasing order of cost.
- Sollin’s algorithm: Select several edges at each stage.
The
Shortest Path
Consider a weighted graph G. The
length of a path in a weighted graph is the sum of the weights of the edges of
this path and the shortest path between two vertices is the minimum length of
the path.
The Dijkstra’s Algorithm finds the shortest path between two vertices
in weighted graph.
AI is thinking...
11. How do you transverse a binary tree? Discuss.
The tree traversal is a way in which each node in the tree is visited exactly once in a symmetric manner.
The binary tree can be traverse in 3 ways:
1.
Pre-order traversal
2.
In-order traversal
3. Post-order traversal
Pre-order Traversal
In Pre-Order traversal, the root node is visited before left child and right child nodes. In this traversal, the root node is visited first, then its left child and later its right child. This pre-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree.
Algorithm:
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Visit root node Step 2: Recursively traverse left sub-tree. Step 3: Recursively traverse right sub-tree. |
.
E.g.
The preorder traversal output of the given above tree is: A B D H I E C F G
In-order Traversal:
In In-Order traversal, the root node is visited between left child and right child. In this traversal, the left child node is visited first, then the root node is visited and later we go for visiting right child node. This in-order traversal is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree. This is performed recursively for all nodes in the tree
Algorithm:
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Recursively traverse left sub-tree. Step 2: Visit root node Step 3: Recursively traverse right sub-tree. |
E.g.
The inorder traversal output of the given tree is: H D I B E A F C G
Post-order Traversal
In Post-Order traversal, the root node is visited after left child and right child. In this traversal, left child node is visited first, then its right child and then its root node. This is recursively performed until the right most node is visited.
Algorithm:
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Recursively traverse left sub-tree. Step 2: Recursively traverse right sub-tree. Step 3: Visit root node |
E.g.
The post-order traversal output of the given above tree is: H I D E B F G C A
AI is thinking...
11. Differentiate between Pre-order and In order traversal.
Pre-order Traversal
In
Pre-Order traversal, the root node is visited before left child and right child
nodes. In this traversal, the root node is visited first, then its left child
and later its right child. This pre-order traversal is applicable for every
root node of all subtrees in the tree.
Algorithm:
|
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Visit root node Step 2: Recursively traverse left
sub-tree. Step 3: Recursively traverse right
sub-tree. |
.
E.g.
The preorder traversal output of the given above tree is: A B D H I E C F G
In-order Traversal:
In
In-Order traversal, the root node is visited between left child and right child.
In this traversal, the left child node is visited first, then the root node is
visited and later we go for visiting right child node. This in-order traversal
is applicable for every root node of all subtrees in the tree. This is
performed recursively for all nodes in the tree
Algorithm:
|
Until all nodes are traversed:- Step 1: Recursively traverse left
sub-tree. Step 2: Visit root node Step 3: Recursively traverse right
sub-tree. |
E.g.
The
inorder traversal output of the given tree is: H D I B E A F C G
AI is thinking...
12. Describe strong and weekly connected graphs with examples. What is weighted graph?
A graph is said to be strongly connected if every pair of vertices(u, v) in the graph contains a path between each other. In an unweighted directed graph G, every pair of vertices u and v should have a path in each direction between them i.e., bidirectional path. The elements of the path matrix of such a graph will contain all 1’s. For e.g.

A graph is said to be weakly connected if there doesn’t exist any path between any two pairs of vertices. Hence, if a graph G doesn’t contain a directed path (from u to v or from v to u for every pair of vertices u, v) then it is weakly connected. The elements of such a path matrix of this graph would be random. For e.g.

Weighted Graph
A weighted graph is a graph G, in which each edge, e, is assigned a non-negative real number, w(e), called the weight of e. For e.g.
AI is thinking...
12. Write short notes on:
(a) Dynamic memory allocation
(b) Game tree
AI is thinking...
12. Write the steps involved in deleting a node in a Binary search tree.
Algorithm to delete the node in BST
struct bnode *delete(struct bnode *root, int item)
{
struct bnode *temp;
if(root==NULL)
{
printf(“Empty tree”);
return;
}
else if(item<root->info)
root->left=delete(root->left, item);
else if(item>root->info)
root->right=delete(root->right, item);
else if(root->left!=NULL &&root->right!=NULL) //node has two child
{
temp=find_min(root->right);
root->info=temp->info;
root->right=delete(root->right, root->info);
}
else
{
temp=root;
if(root->left==NULL)
root=root->right;
else if(root->right==NULL)
root=root->left;
free(temp);
}
return(temp);
}
Finding minimum element function:
struct bnode *find_min(struct bnode *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return0;
else if(root->left==NULL)
return root;
else
return(find_min(root->left));
}
E.g.
1. Deleting leaf Node
2. Deleting node with right child
3. Deleting node with left child
4. Deleting a node having both right and left child
AI is thinking...
13. Write short notes on:
a. Tree traversal
b. Circular queue
a) Tree Traversal
The tree traversal is a way in which each node in the tree is visited exactly once in a symmetric manner.
The binary tree can be traverse in 3 ways:
1. Pre-order traversal
2. In-order traversal
3. Post-order traversal
1. Pre-order Traversal: In Pre-Order traversal, the root node is visited before left child and right child nodes. In this traversal, the root node is visited first, then its left child and later its right child. This is performed recursively for all nodes in the tree. For e.g.
The preorder traversal output of the given above tree is: A B D H I E C F G
2. In-order Traversal: In In-Order traversal, the root node is visited between left child and right child. In this traversal, the left child node is visited first, then the root node is visited and later we go for visiting right child node. This is performed recursively for all nodes in the tree. For e.g.
The inorder traversal output of the given tree is: H D I B E A F C G
3. Post-order Traversal: In Post-Order traversal, the root node is visited after left child and right child. In this traversal, left child node is visited first, then its right child and then its root node. This is recursively performed until the right most node is visited. For e.g.
The post-order traversal output of the given above tree is: H I D E B F G C A
Circular Queue is a linear data structure in which the operations are performed based on FIFO (First In First Out) principle and the last position is connected back to the first position to make a circle.
Graphical representation of a circular queue is as follows.
AI is thinking...
13. Explain the Kruskal‟s algorithm.
Kruskal's Algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph. The main target of the algorithm is to find the subset of edges by using which, we can traverse every vertex of the graph.
The Kruskal's algorithm is given as follows:
1. List all the edges of G with non-decreasing order of their weights.
2. Select an edge of minimum weight. This will be the first edge of T.
3. At each stage, select an edge of minimum weights from all remaining edges of G if it doesn’t form a cycle with previously selected edges in T. Then add the edge to T.
4. Repeat step 3 until n-1 edges have been selected.
(1, 6) | (4, 3) | (2, 7) | (2, 3) | (7, 4) | (4, 5) | (5, 7) | (5, 6) | (1, 2) |
7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 | 18 |
Pick edge (1, 6): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (4,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,7): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (7,4): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (4,5): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (5,7): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (5,6): No cycle is formed, include it.
.
Since the number of edges included equals (n– 1), the algorithm stops here.
AI is thinking...
13. Discuss the Kruskal's algorithm with example.
Kruskal's Algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted graph. The main target of the algorithm is to find the subset of edges by using which, we can traverse every vertex of the graph.
The Kruskal's algorithm is given as follows:
1. List all the edges of G with
non-decreasing order of their weights.
2. Select an edge of minimum weight.
This will be the first edge of T.
3. At each stage, select an edge of
minimum weights from all remaining edges of G if it doesn’t form a cycle with
previously selected edges in T. Then add the edge to T.
4. Repeat step 3 until n-1 edges have been selected.
|
(1, 6) |
(4, 3) |
(2, 7) |
(2, 3) |
(7, 4) |
(4, 5) |
(5, 7) |
(5, 6) |
(1, 2) |
|
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
17 |
18 |
Pick edge (1, 6): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (4,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,7): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (2,3): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (7,4): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (4,5): No cycle is formed, include it.
Pick edge (5,7): Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
Pick edge (5,6): No cycle is formed, include it.
Since the number of edges included equals (n– 1), the algorithm stops here.
AI is thinking...
